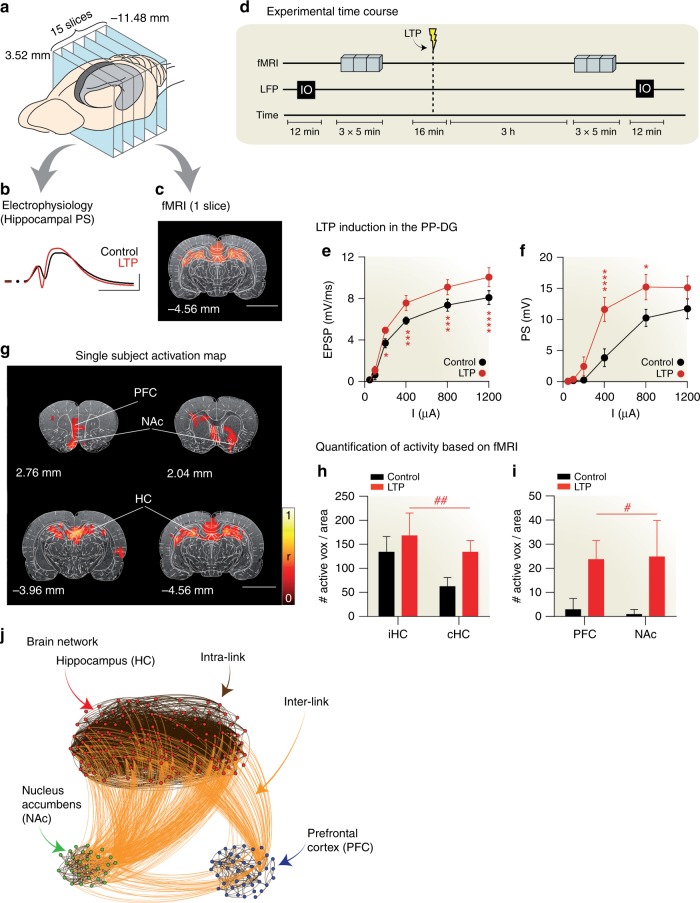
Fig. 1.
Experimental protocol and generation of brain network. a Schematic representation of the imaging planes (blue). The hippocampus (HC) is highlighted in gray. Numbers indicate z coordinate in mm from bregma. b Representative evoked population spike (PS) in the dentate gyrus before (black) and after (red) LTP induction. c Representative fMRI maps across the HC during perforant path stimulation overlaid on an anatomical T2-weighted image with atlas parcellations (see Supplementary Note 2). Color indicates significant correlation (p < 0.005 corrected). d Time course of the experiment. Input/output (I/O) response curves are recorded in the local-field potentials (LFP). fMRI signals are collected during low-frequency (10 Hz) test stimulations before and 3 h after LTP induction. e Field excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) slope and, f population spike (PS) amplitude before (black) and after (red) LTP. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA (n = 5, α = 0.05) reveals significant effects of LTP in both measures (F1,24 = 27.82, p < 0.0001, and F1,24 = 59.89; p < 0.0001 for PS and EPSP, respectively). Mean ± SEM. Post-hoc Bonferroni: *p < 0.1; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 g Representative fMRI maps in one animal after LTP induction. Color code as in (c) (p < 0:005; see Supplementary Note Fig. 1 for group activation maps and Supplementary Note 2 for details). Size bar corresponds to 0.5 mm. h, i Number of active voxels per selected region in control (black) and LTP (red) conditions in hippocampal (h) and extra-hippocampal areas (i). The stimulated region is the ipsilateral hippocampus (iHC); two-way repeated-measures ANOVA (n = 7, α = 0.05) reveals significant effects for LTP in hippocampal (F1,12 = 15.72, ##p = 0.0019) and extrahippocampal regions (F1,12 = 7.426, #p = 0.0184), with no interaction between regions (F1,12 = 0.00242, p = 0.9616 and F1,12 = 1.518, p = 0.2415 for hippocampal and extra-hippocampal regions, respectively). Mean ± SEM. j Brain network formed by the HC, NAc, and PFC for the animal in (g). The brain network is formed by intra-network interactions and inter-network interactions inferred from fMRI correlation data (Supplementary Note 3)