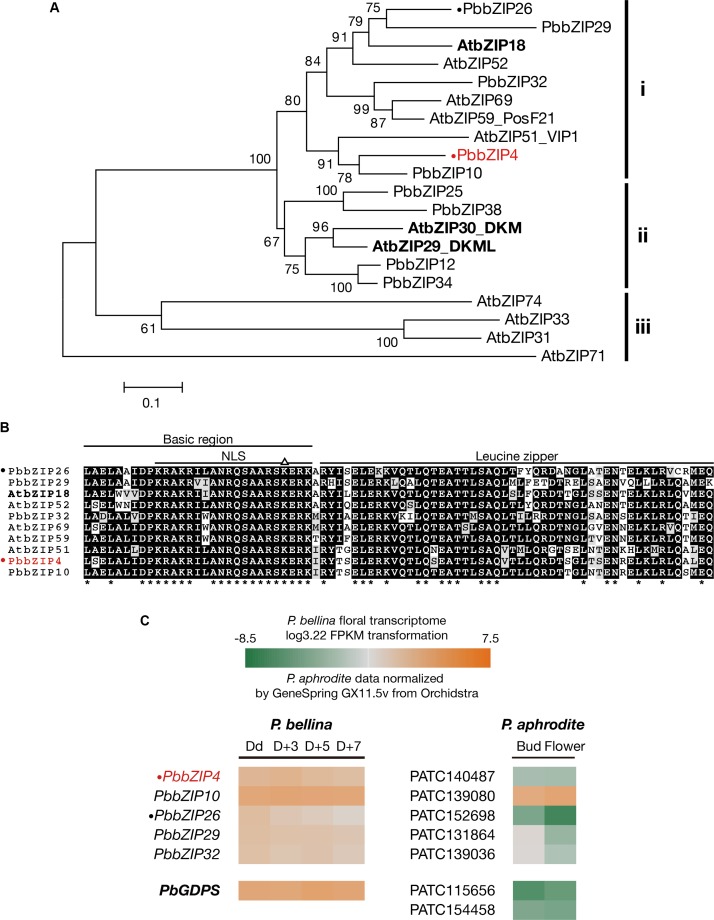
FIGURE 5.
Analysis of bZIP group I TFs in P. bellina floral transcriptome. (A) Phylogenetic tree inferred from the amino sequences of the nine bZIP group I TFs with the ones in Arabidopsis. The three subgroups were divided based on their phylogenetic relationship. Three AtbZIPs isolated by Y1H screening were seen in bold. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of subgroup i proteins in (A). Asterisks (∗) below the alignment indicate the consensus residues in all sequences. The triangle (∆) above the alignment indicates the lysine replacement of the conserved arginine residue in the basic region of group I of bZIP family. (C) Comparison of the expression levels of five bZIP TFs between two Phalaenopsis transcriptomes. Gene expression levels in P. bellina transcriptomes were transformed by log3.22 FPKM in four floral developmental stages, including Dd, D + 3, D + 5, and D + 7 (Chuang et al., unpublished), while the levels of two floral stages of flower bud and flower in P. aphrodite transcriptomes were analyzed via microarray experiments stored in Orchidstra (Su et al., 2013a). Expression levels of putative genes are represented by a color gradient from orange to gray to green. Two PbbZIPs for transient assays, PbbZIP4 and PbbZIP26, are labeled with a dot (•). PbbZIP4 was especially shown in red. The expression levels of PbGDPS (in bold) was also included for comparison.