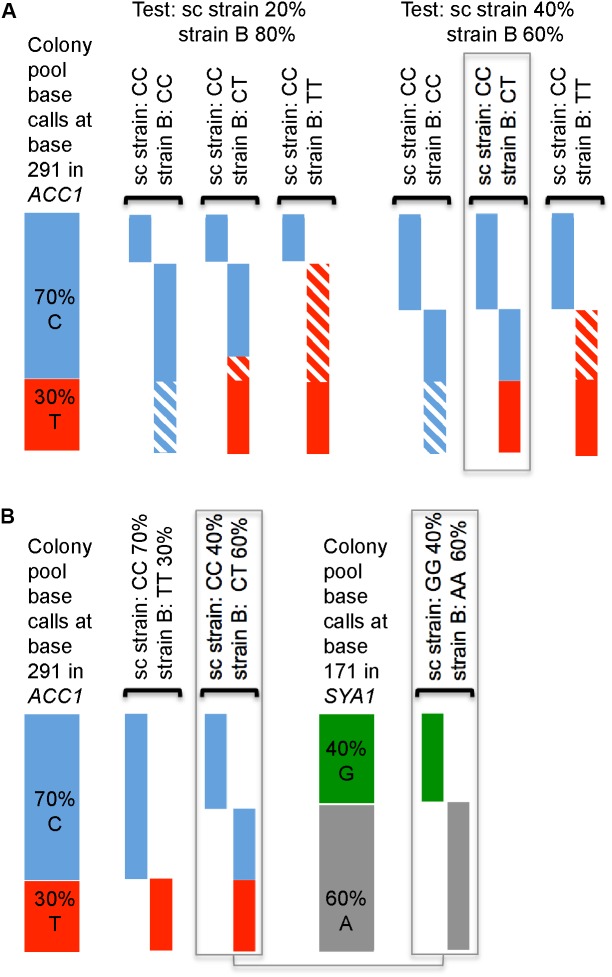
FIGURE 1.
Principle of deducing the frequency and genotypes of two strains from base calls when sequencing DNA prepared from a mixture of colonies. (A) Predicted allele frequencies assuming that either 20 or 40% of cells in the sample were from the strain represented by the directly sequenced colony (sc strain; CC, i.e., C-homozygous) and assuming three possible genotypes of strain B (shown on top, above brackets), which are compared to observed base calls (at position 291 in the ACC1 amplicon; 70% C/30% T; shown on the left). Contributions of each strain to expected base calls are visualized as boxes under the genotypes; striped parts of the bars indicate the differences between expected and observed frequencies. (B) Two possible frequencies of strain B would explain the pool base calls at ACC1 291, but only one frequency of strain B (60%) explains the base call frequencies at position 171 in the SYA1 amplicon.