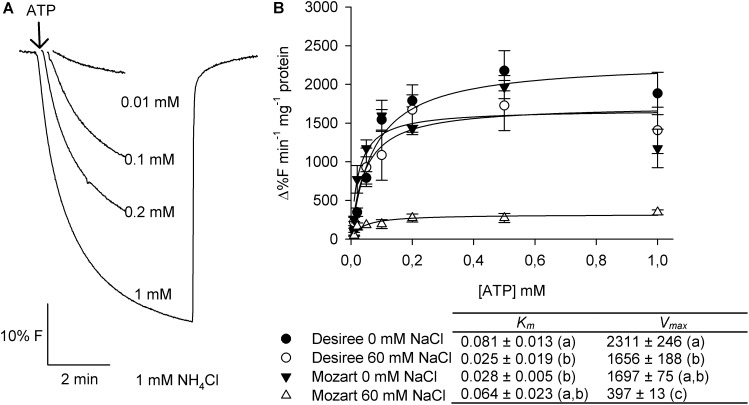
FIGURE 4.
Effect of salt stress on the ATP-dependent proton transport activity in tonoplast vesicles isolated from potato leaves. (A) Representative traces of proton pump activity in tonoplast vesicles isolated from leaves of the cultivar Desiree. The V-H+-ATPase was activated by the addition of increasing concentrations of ATP to the assay medium containing 20 μg protein of membrane vesicles. After equilibration of the quench, 1 mM NH4Cl was added to release the quench. (B) Dose response curves of the initial rates of proton pump activity of the V-H+-ATPase in dependence of the substrate ATP concentration for both cultivars treated with and without 60 mM NaCl. The curves were fitted with the Michaelis–Menten equation with the aid of SigmaPlot software package. The average Km and Vmax values as shown in the table were calculated from the fit of each independent experiment (n = 3 ± SEM). Different letters indicate a statistically significant treatment effect (one-way ANOVA; P < 0.05). A two-way ANOVA showed a treatment × cultivar interaction effect for both Km and Vmax (P< 0.05).