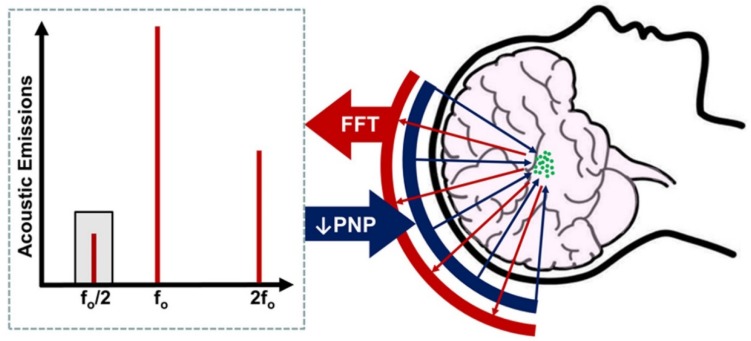
Figure 1.
Basic principle of acoustic emissions monitoring for control of blood-brain barrier opening with focused ultrasound. After intravenous microbubble injection, focused ultrasound (blue arrows) is applied from a phased-array transducer, activating microbubbles (green circles) in the treatment volume. Acoustic emissions from the oscillating microbubbles (red arrows) are monitored by a separate set of elements within the array. The peak-negative pressure (PNP) of applied focused ultrasound is steadily increased until subharmonic (i.e. f0/2; grey shading) emissions are detected. PNP is then reduced by a fixed amount, typically 50%, to ensure safe and reversible BBB opening in the treatment volume.