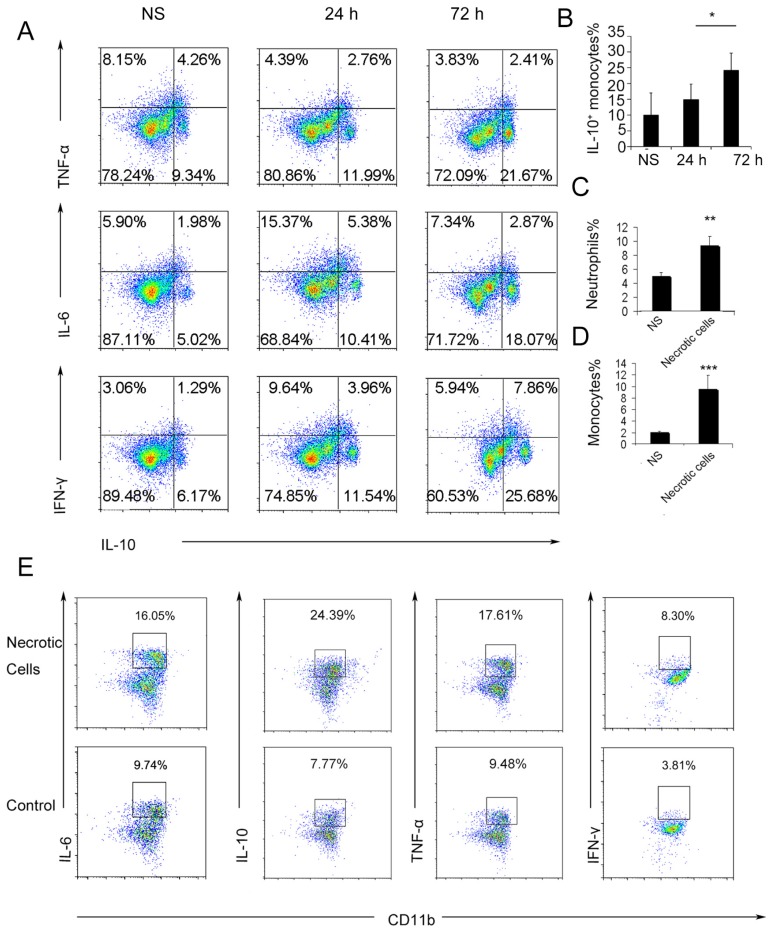
Figure 2.
Ly6C+ inflammatory monocytes adopted a dual phenotype after being stimulated with necrotic lung cells. (A) DOTAP liposomes or normal saline as a control were injected into C57BL/6 mice, and the mice were sacrificed 24 or 72 h after the injection. The intracellular cytokines of Ly6C+ inflammatory monocytes were analysed by flow cytometry. First, the cells were gated on CD45+CD11b+Ly6C+ monocytes. Intracellular cytokine staining for IL-10 in conjunction with TNF-α, IL-6 and IFN-γ was conducted. Numbers represent the percentage of cells in each gate (n=9). (B) Average percentage of IL-10+ inflammatory monocytes in the control and at 24 and 72 h after dosing (n=9). (C-D) Analysis of inflammatory neutrophils and monocytes 48 h after an intravenous injection of 1×106 necrotic lung cells (n=3). (E) Monocytes isolated from bone marrow were stimulated with necrotic lung cells for 4 h in the presence of brefeldin A. Intracellular cytokine staining for IL-10, TNF-α, IL-6 and IFN-γ; first, the cells were gated on CD45+CD11b+Ly6C+ monocytes (n=3). Data are representative of three independent experiments, and the results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. Statistical comparisons were performed using Student's t-test or Dunnet's t-test (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.005).