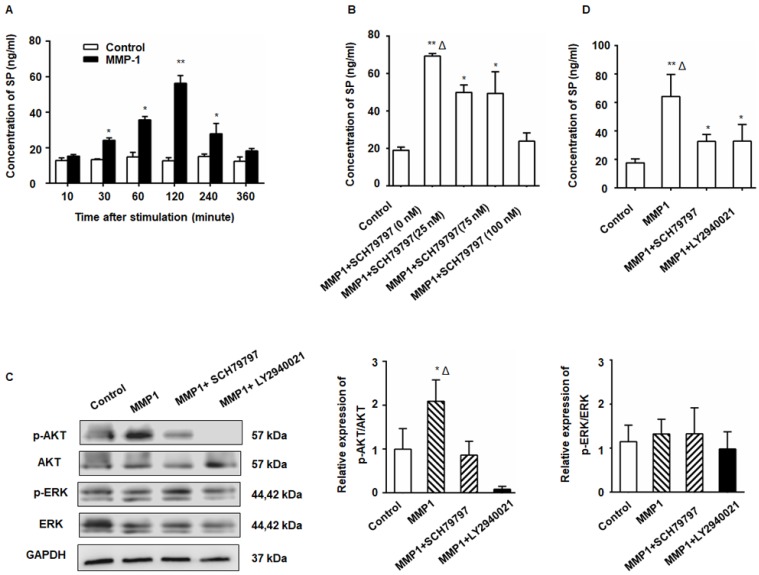
Figure 2.
The MMP1/PAR1 axis induced DRG-releasing SP by activating Akt. (A) Thirty minutes after MMP1 (5 nM) stimulation, the SP concentration in the DRG supernatant began to increase and the peak concentration was detected at 2 h. The concentration of SP protein decreased almost to baseline levels at 6 h. (B) DRG were incubated in DMEM with MMP1 (5 nM) and different concentrations of PAR1 antagonist SCH79797 (0, 25, 50, and 100 nM) for 2 h, and the SP concentration in the supernatant was measured by ELISA. The MMP1-induced SP release was inhibited by SCH79797. (C) MMP1 induces DRG-releasing SP via MMP1/PAR1/AKT. After MMP1 stimulation, p-Akt increased in the DRG, whereas the PAR1 antagonist SCH79797 attenuated the phosphorylation of Akt. LY2940021 (Akt pathway inhibitor) was used as a positive control. The expression of ERK1/2 and p-ERK1/2 remained unchanged. (D) ELISA showed that the upregulation of SP induced by MMP1 was attenuated by treatment with the PAR1 antagonist or the Akt pathway inhibitor. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01 compared to the control. Δ P < 0.05 compared to the SP+ SCH79797 group.