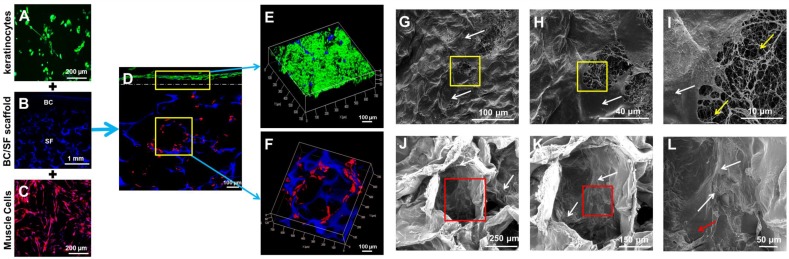
Figure 4.
In vitro incubation of engineered urethral tissue. (A, C) Immunofluorescence staining of lingual keratinocytes and muscle cells. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of the SF-BC scaffold with DAPI. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of a cross-section of a cell-seeded SF-BC scaffold. (E) Immunofluorescence staining demonstrating that keratinocytes formed a compact confluent keratinocyte layer. (F) Immunofluorescence staining demonstrating that muscle cells invaded the SF-BC scaffold and dispersed throughout the porous polymer. (G-I) SEM analysis of keratinocytes on the compact surface of the SF-BC scaffold. (J-L) SEM analysis of muscle cells located inside the porous network that had grown along the SF wall. The white arrow indicates the cells, the yellow arrow indicates the nanofiber and the red arrow indicates the SF.