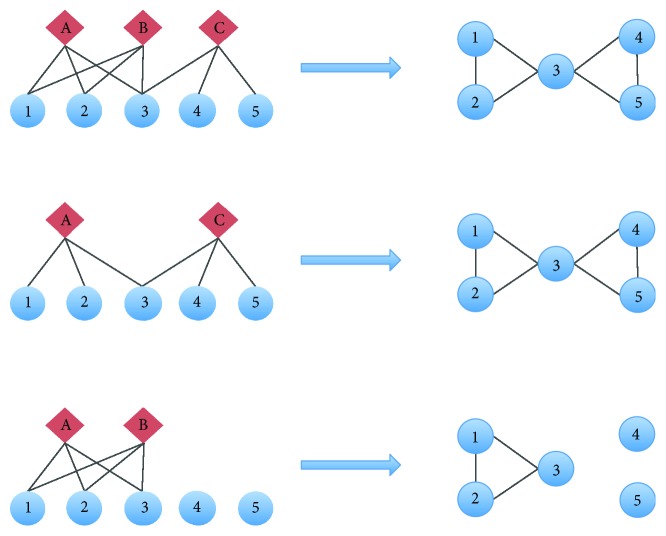
Figure 1.
In this figure, we show a simple bipartite graph with 3 top nodes (A to C) and 5 bottom nodes (1 to 5). The projection of bottom nodes is shown on the right side. If node B is removed, no link in the projection is lost, as all bottom nodes connected through B are also connected through A; therefore, B is redundant. Meanwhile, removing node C causes the loss of connections of bottom nodes 4 and 5; therefore, C is nonredundant.