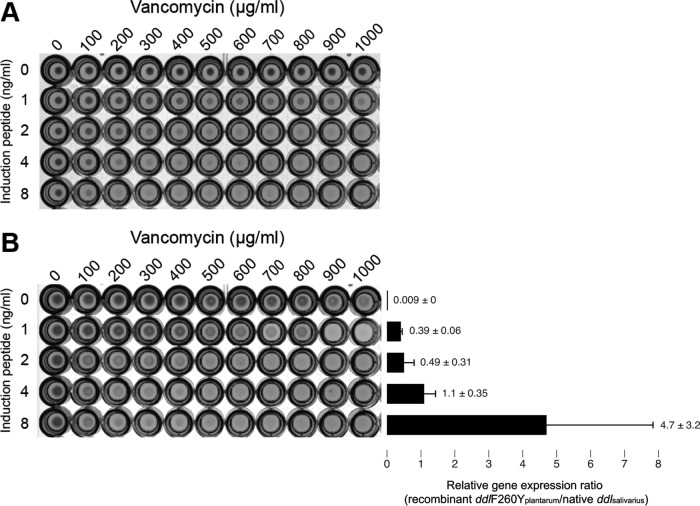
FIG 3.
Vancomycin sensitivity depends on the Ddl dipeptide expression level. (A) Assessment of the vancomycin MIC following titration of induction peptide (0, 1, 2, 4, or 8 ng/ml) in L. plantarum BAA-793 harboring pSIP-ddlF260Yplantarum. (B) (Left panel) Assessment of the vancomycin MIC following titration of induction peptide (0, 1, 2, 4, or 8 ng/ml) in L. salivarius CCUG 47825 harboring pSIP-ddlF260Yplantarum. Data in panels A and B are representative of results from three biological replicates. The differences between replicates in the recorded MICs were no greater than 100 μg/ml. The pictures of the MIC panels have been modified from the original by removing two rows—corresponding to 0.25 and 0.5 ng/ml induction peptide—which were originally located below the row corresponding to 0 ng/ml induction peptide. (Right panel) We determined for each concentration of the induction peptide the corresponding ratio of ddlF260Yplantarum and the native L. salivarius ddl transcripts by quantitative real-time PCR. Numbers next to the bars indicate the ratios of the transcript levels of ddlF260Yplantarum and L. salivarius ddl relative to those of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) housekeeping gene, which were normalized to the levels determined for the untreated sample (0 ng/ml). Error bars represent standard deviations of results from three biological replicates.