Fig. 7.
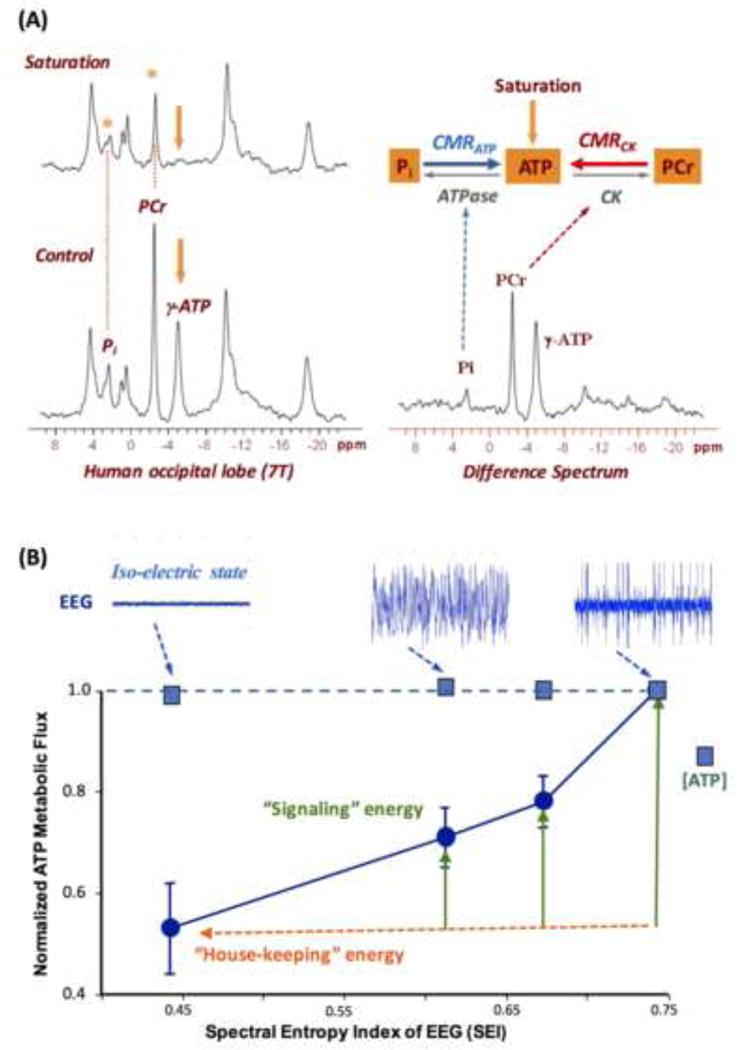
(A) In vivo 31P spectra (left panels) acquired from a healthy human occipital lobe in the absence (control) and presence of γ-ATP resonance saturation, and the difference spectrum (right panel). The intensity reduction in Pi and PCr resonance can be used to calculate the value of CMRATP and CMRCK, respectively. Adapted from the reference of Lei et. al. [8]. (B) Correlation of the rat brain EEG activity level (top tracers) versus normalized CMRATP and cerebral ATP concentration measured under varied brain states using different anesthetics and/or doses. The EEG signal was quantified by the spectral entropy index (SEI). It shows a strong and positive correlation between the EEG amplitude and CMRATP while maintaining the ATP homeostasis across a wide range of neurophysiology condition. Adapted from the reference of Du et. al. [5].
