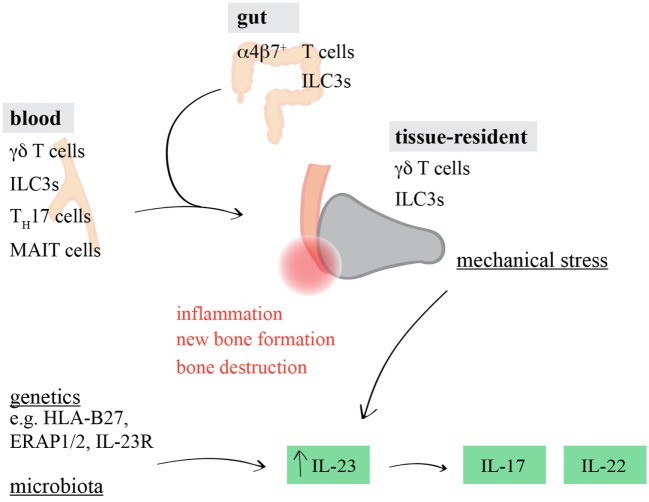
Figure 1.
Involvement of interleukin (IL)-17/IL-22-producing lymphocytes in spondyloarthritis (SpA)-associated inflammation. Genetic and epigenetic predisposition, altered microbial composition, and entheseal microdamage can influence the induction and progression of tissue inflammation in SpA. In addition to tissue-resident γδ T cells and ILC3s, circulating and/or gut-derived γδ T cells, ILC3s, TH17 cells, or mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells might promote IL-23-driven joint inflammation by producing increased amounts of IL-17 and IL-22.