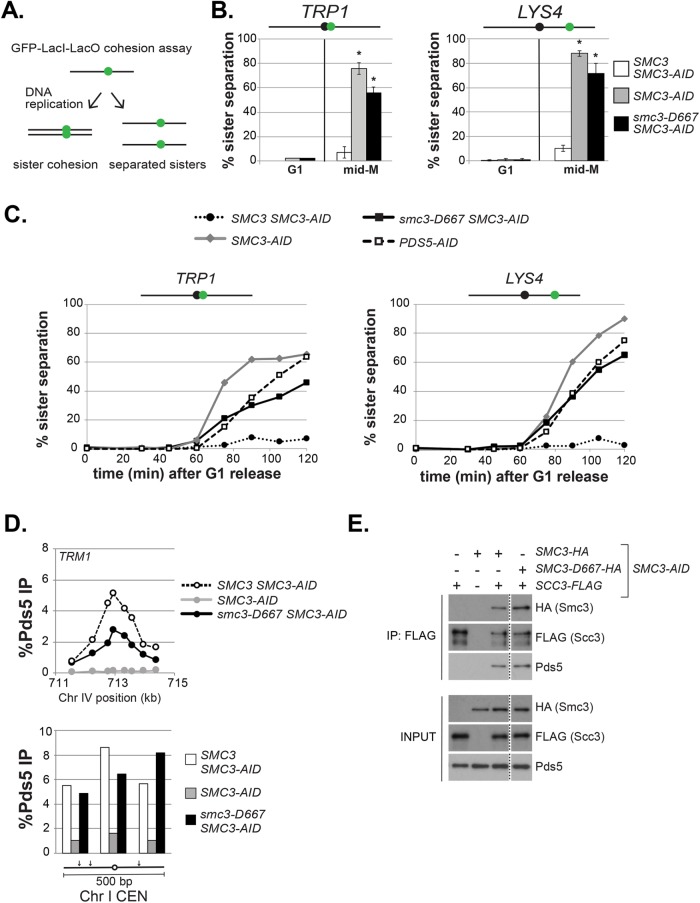
FIGURE 3:
The smc3-D667 mutant exhibits a cohesion maintenance defect. (A) Schematic of cohesion loss assay using loci tagged with GFP-LacI. After replication, cells with cohesion have a single GFP focus, whereas cells where cohesion is lost have two GFP foci. (B) Cohesion loss at CEN-proximal TRP1 and CEN-distal LYS4 loci in mid–M phase–arrested cells. Haploid strains were arrested in G1, depleted of Smc3p-AID, and then synchronously released from G1 and rearrested in mid–M phase under depletion conditions as described in Figure 2A. LacO arrays integrated at TRP1 (left) in haploid SMC3-AID yeast alone (BRY676) or also containing wild-type SMC3 (BRY678) or smc3-D667 (BRY680). LacO arrays integrated at LYS4 (right) in SMC3-AID yeast alone (VG3651-3D) or containing wild-type SMC3 (BRY474) or smc3-D667 (BRY482). Samples were collected from G1-arrested auxin-treated cells and mid–M phase–arrested cells and scored for cohesion. The percentage of cells with two GFP foci (sister separation) were averaged from two independent experiments and plotted. Cells (100–200) were scored per sample at each time point. Error bars represent SD. *p < 0.05 when tested against SMC3 SMC3-AID % sister separation in mid–M (t test, two-tailed). (C) Time course to assess the kinetics of cohesion loss. Haploid strains were arrested in G1, treated with auxin, and synchronously released into mid–M phase arrest in auxin containing media as described in Figure 2A. Samples were collected in G1 and every 15 min starting 30 min after G1 release and fixed to assess cohesion loss and DNA content. Data are shown as the percentage of cells with separated sisters. Cells (100–200) were scored for cohesion for each time point. DNA content was assessed by flow cytometry and shown in Supplemental Figure 4A. The left side shows cohesion loss at the CEN-proximal TRP1 locus. Haploid strains SMC3 SMC3-AID (BRY678), SMC3-AID (BRY676), smc3-D667 SMC3-AID (BRY680), and PDS5-AID (BRY815). The right side shows cohesion loss at the CEN-distal LYS4 locus. Haploid strains SMC3 SMC3-AID (BRY474), SMC3-AID (VG3651-3D), smc3-D667 SMC3-AID (BRY482), and PDS5-AID (TE228). (D) ChIP to assess Pds5p binding to chromosomes. Haploid strains SMC3 SMC3-AID (BRY474), SMC3-AID (VG3651-3D), and smc3-D667 SMC3-AID (BRY482) arrested in mid–M phase according to the regimen in Figure 2A were fixed and processed for ChIP using polyclonal anti-Pds5p antibody. Pds5p binding was assessed at the CAR TRM1 (top), and centromeres I and XIV (bottom). (E) Smc3-D667p supports assembly of cohesin containing Pds5p and Scc3-3FLAGp. Haploid strains SMC3-AID (VG3561-3D), SCC3-3FLAG SMC3-AID (BRY607), SMC3-6HA SMC3-AID (BRY604), SCC3-3FLAG SMC3-6HA SMC3-AID (BRY621), and SCC3-3FLAG smc3-6HA-D667 SMC3-AID (BRY625) cells were grown as described in Figure 2A. Protein extracts were made and Scc3p immunoprecipitated using anti-FLAG antibody, subjected to SDS–PAGE and Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. Dotted line indicates where an irrelevant lane was removed.