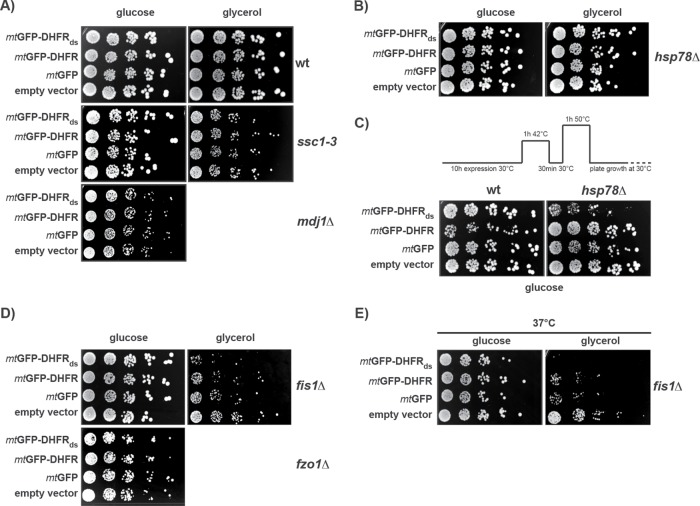
FIGURE 6:
Analysis of aggregate proteotoxicity in different mutant cells. Cellular factors involved in IMiQ formation. (A–E) Growth rates of mutant yeast cells expressing mtGFP-DHFRds or control proteins. After galactose induction for 10 h, cells from the indicated mutant strains were spotted on selective plates containing fermentable (2% glucose) or nonfermentable carbon source (3% glycerol) and incubated at 30°C to assess mitochondrial function. (A) Hsp70 chaperone system. Temperature-sensitive mutant ssc1–3 cells (Gambill et al., 1993) were pretreated for 1 h at 37°C to induce the nonpermissive phenotype. The mdj1∆ deletion strain was respiration deficient and did not grow on nonfermentable carbon sources. (B) Growth analysis of hsp78∆ deletion cells. (C) Analysis of acquired thermotolerance in WT and hsp78∆ deletion cells expressing mtGFP-DHFRds or control proteins for 10 h. After protein expression at 30°C, cells were subjected to a short heat shock and recovery as indicated. Cells were then incubated at a lethal temperature of 50°C for 1 h and spotted on selective plates containing 2% glucose. (D) Growth analysis of fis1∆ and fzo1Δ deletion cells. (E) Growth of fis1Δ cells expressing the destabilized reporter protein for 10 h under mild thermal stress. Cells were spotted as described above and incubated at 37°C.