Figure 1.
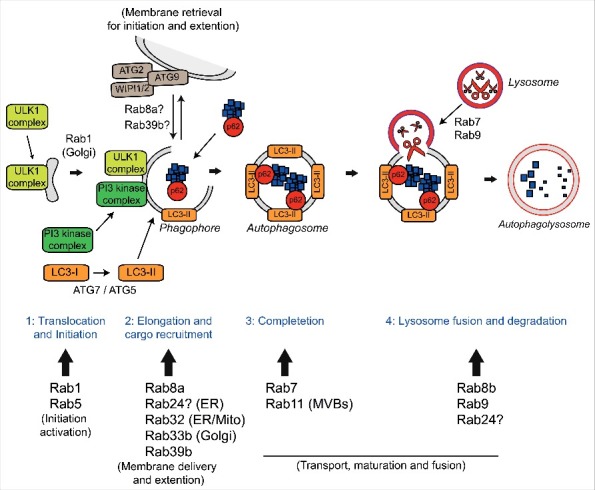
Autophagy and the Rab GTPases. The four stages of autophagy are indicated with the different Rabs involved at each stage. 1) Translocation of the ULK1 initiation complex to the phagophore is the first step in autophagy initiation. Rab1a mediates trafficking of the ULK1 complex to the phagophore and is involved in delivery of ATG9 positive membranes to the site of phagophore formation. Rab5 is involved in translocation of the Class III PI3 kinase complex and delivery of LC3-II. 2) Elongation of the phagophore membrane requires the Class III PI3 kinase complex. Rab8a, Rab24, Rab32, Rab33b and Rab39b are all involved in autophagosome formation and may aid in elongation by the delivery of additional membrane via ATG9/ATG2/WIPI1/2. Autophagy substrates are recruited to the growing phagophore by autophagy receptors such as p62/sequestosome-1 and optineurin. Autophagy receptors bind ubiquitin on the substrates and LC3-II on the nascent phagophore resulting in substrate delivery. 3) After completion and closure, autophagosomes are transported to allow fusion with the lysosome. Rab7 is involved in autophagosome transport while Rab11 delivers multi-vesicular bodies (MVBs) to the autophagosome, which appears to be required for maturation. 4) Autophagosome fusion with the lysosome allows degradation of the autophagic substrates. Rab7, Rab8b and Rab9 are involved in the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes, a process that may also require Rab24. Finally, autophagic substrates are degraded by the acid hydolases of the lysosome and recycled back to the cytoplasm.
