Figure 3.
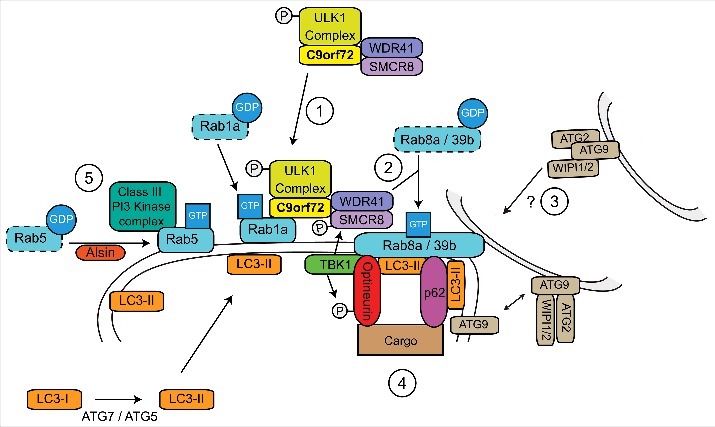
C9orf72 is a central hub in a Rab cascade pathway during autophagy induction. 1) C9orf72 controls the Rab1a-dependent translocation of the ULK1 initiation complex to the site of phagophore formation by interacting with the ULK1 complex and active GTP-Rab1a. 2) At the site of phagophore formation, the C9orf72/SMCR8/WDR41 complex functions as a GEF for Rab8a and Rab39b. 3) Active Rab8a and Rab39b may be involved in delivery of additional membrane to the site of phagophore formation by retrieval of ATG9 positive membranes. Additional membrane allows elongation of the nascent phagophore and formation of an autophagosome. 4) The autophagy receptors p62/sequestosome-1 and optineurin interact with Rab8a and Rab39b, promoting nucleation and site specific recruitment of autophagic substrates to the growing phagophore. Furthermore, Rab8a also recruits TBK1, leading to phosphorylation of optineurin, SMCR8 and ULK1. The phosphorylation of optineurin enhances its interaction with LC3-II, facilitating substrate delivery and the progression of autophagy. 5) The Class III PI3 Kinase complex is also required for autophagosome formation. Rab5, activated by Alsin, delivers the PI3 Kinase complex to the phagophore and also facilitates the recruitment of the ATG7-ATG5 conjugation system required for LC3-II formation.
