Figure 2.
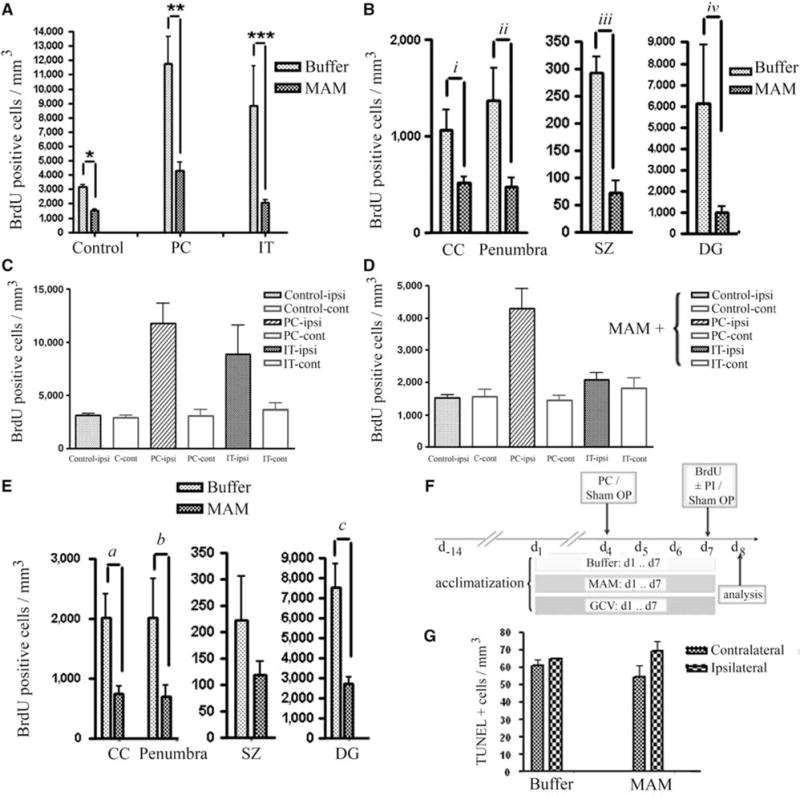
Quantification analysis of BrdU-positive progenitor cells. (A) Reduction of BrdU-positive cells (cells/mm3) after MAM treatment in control animals (sham OP), preconditioning (PC), and ischemic tolerance (IT). (B) Attenuation of BrdU-positive cells with MAM treatment occurred in CC, DG, subependymal zone (SZ) as well as in the penumbra (number of BrdU-positive cells present at the hypoperfused area in the vicinity of ischemic border, excluding subependymal zone (SZ), CC, and DG), after tolerance induction (a preconditioning stimulus (15 mins MACO) followed by prolonged ischemia (60 mins MACO after 72 h)). (C, D) The number of BrdU-positive cells is greater in ipsilateral than in contralateral sides in buffer-treated (C) and MAM-treated (D) animals in response to preconditioning (PC, 15 mins MACO), ischemic tolerance (IT, 15 mins MACO followed by 60 mins MACO after 72 h) and in buffer-treated controls (note scale difference between C and D). Significance showed in Panel “A”. (E) Comparison of the BrdU-positive cells in CC, penumbra, SZ, and DG after preconditioning stimulus (15 mins MACO) in buffer- and MAM-treated animals. (F) Time line: all the animals were acclimatized for 2 weeks. Buffer, MAM, or GCV (GCV) was applied subcutaneously for 7 days and BrdU (50 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally at day 7. (G) Bars show the number of TUNEL-positive cells in both contralateral and ipsilateral sides of the brain of control animals (treated with buffer) or animals treated with MAM for 7 days. No significant changes were observed in the number of TUNEL-positive cells in MAM-treated animals compared with the control. *P = 0.0029, **0.009, ***P = 0.0048, iP = 0.0023, iiP = 0.0217, iiiP = 0.0088, ivP = 0.0059, aP = 0.0297, bP = 0.0139, and cP = 0.0059.
