Figure 6.
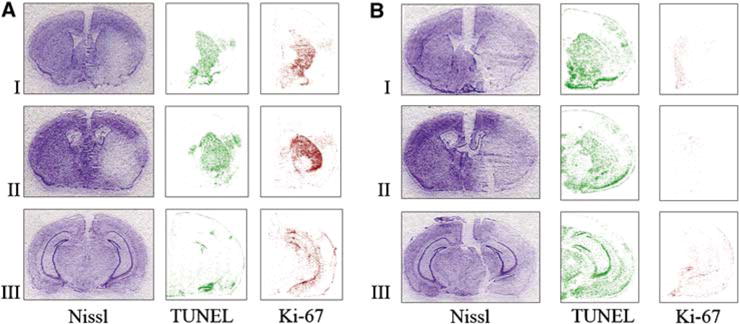
Comparison of the extent of injury (Nissl) and number of proliferating (Ki-67) and apoptotic cells (TUNEL) in MAM-treated animals (B) and control group (A) after attempting to induce tolerance: a preconditioning stimulus (15 mins MACO) followed by prolonged ischemia (60 mins MACO after 72 h). Nissl staining shows that the infarct size is significantly larger in MAM animals subjected to the ischemic tolerance paradigm (B) compared with buffer-treated controls, which show ischemic tolerance (A). The number of TUNEL-positive cells was increased after MAM treatment, whereas the number of Ki-67-positive proliferating progenitors was significantly reduced in MAM-treated animals (B). Brain sections were obtained from the following regions: I = + 0.50±0.20, II = −0.50±0.20, and III = −2.40±0.20 mm from the bregma.
