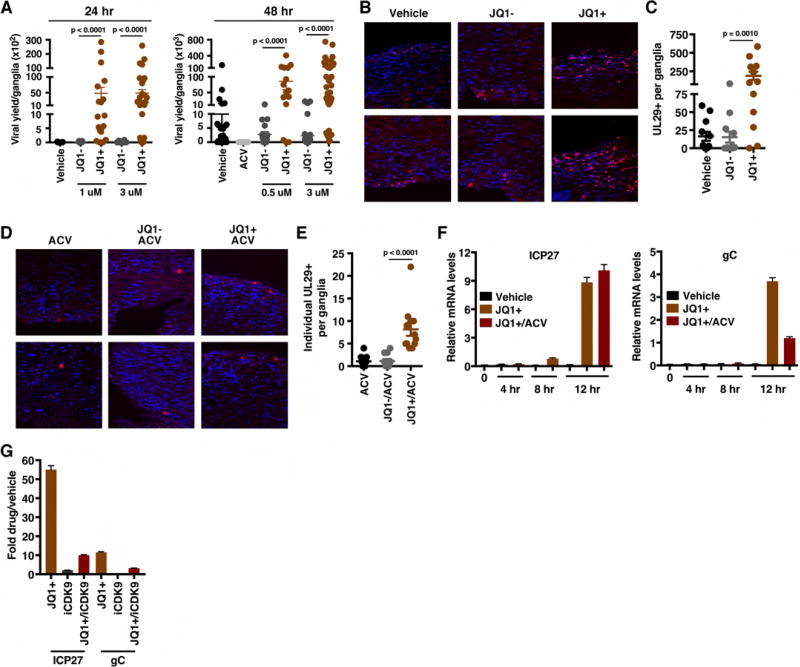
Figure 6. BET inhibitors drive viral reactivation in the mouse ganglia explant model system.
(A) Viral yields from latently infected trigeminal ganglia explanted in the presence of the BRD4-BET inhibitor JQ1+ or control compounds (Vehicle, JQ1−) for 24 or 48 h. Data are yields from individual ganglia, n > = 15. (B) Trigeminal ganglia from latently infected mice were explanted in the presence of JQ1+ or controls (DMSO, JQ1−) for 48 h. Sections were stained for UL29 (HSV lytic ss-DNA binding replication protein, ICP8). (C) The numbers of UL29+ cells per ganglia, n = 12. (D–E) Trigeminal ganglia from latently infected mice were explanted in the presence of acyclovir (ACV) alone or in combination with JQ1+ or JQ1− for 48 h. Ganglia sections were stained for UL29 and the numbers of individual UL29+ cells per ganglia were quantitated, n = 12. (F) Trigeminal ganglia from latently infected mice were explanted in the presence of Vehicle, JQ1+, or JQ1+ and ACV. Viral (ICP27, gC) mRNA levels were determined at 4, 8, and 12 h post explant. (G) Trigeminal ganglia from latently infected mice were explanted in the presence of JQ1+ (1 uM), iCDK9 (0.1 uM), or JQ1+ and iCDK9. Viral mRNA levels were determined at 12 h post explant. (F–G) Samples were normalized based on the levels of cellular GAPDH mRNA. Data are means +/− s.e.m., n = 3 pools of 5 ganglia per group. See also Figure S7.