Figure 4.
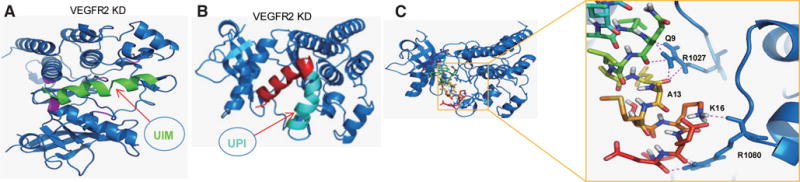
Molecular modeling to study the interaction between UIM or UPI with VEGFR2 kinase domain (VEGFR2-KD). The 3D models of UIM and UPI were predicted using the PEP-FOLD program with 200 computational simulations. The best score models of UIM and UPI were docked into VEGFR2-KD respectively using the ClusPro2.0 program. (A) Ribbon representation of the interaction between UIM and VEGFR2-KD, which are colored green and blue, respectively. The interaction residues His891, His816, Arg1022, Arg1027, and Arg1080 on the hairpin-shaped binding cleft of VEGFR2-KD are denoted in pink;[17,19] (B) Ribbon representation of the association between UPI peptide and VEGFR2-KD. In the same manner as UIM:VEGFR2-KD, UPI binds into the same binding pocket of VEGFR2-KD. VEGFR2-KD is denoted in blue. In UPI peptide, UIM is denoted in red, and the inner plasma membrane anchoring peptide and a tumor homing peptide (iRDG) are denoted in cyan; (C) Cartoon representation of the model of UIM-VEGFR2 complex. VEGFR2 is denoted in blue and shown as a ribbon; UIM is denoted in multicolor and shown as a stick (left). On the right: A close-up view of interaction residues between UIM and VEGFR2 is shown in the right panel. The key residues Q9, A13, and K16 of UIM form hydrogen bonds with R1027 and R1080 of VEGFR2.[19]
