Figure 9.
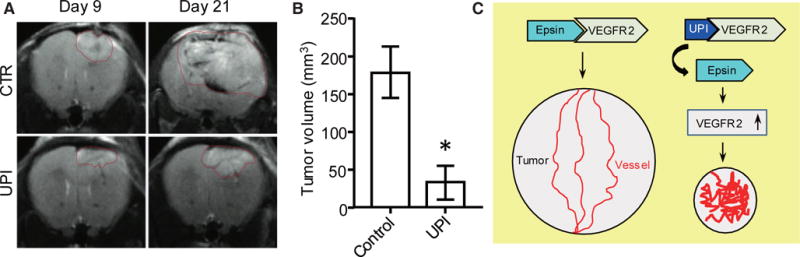
UPI peptide treatment significantly retards tumor growth in glioma tumor models. GL261 glioma cells (2 × 104) were implanted to the right forebrain of C57BL/6 mice. At day 9, UPI peptide was administered by intravenous injection at 20 mg/kg dosage every alternate day. Gliomas were monitored via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). (A) Representative MRI images. (B) Statistical analysis of tumor volume of terminal mice treated by control or UPI peptide; n = 5 in each group, Student t-test, *P < 0.001 vs. control. (C) Sketch of the UPI peptide therapeutic mechanism. UPI administration inhibits Epsin-VEGFR2 interaction in vivo, promotes non-functional tumor angiogenesis, and retards tumor growth
