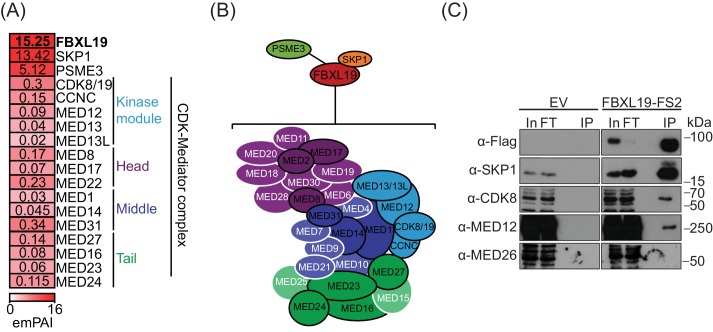
(
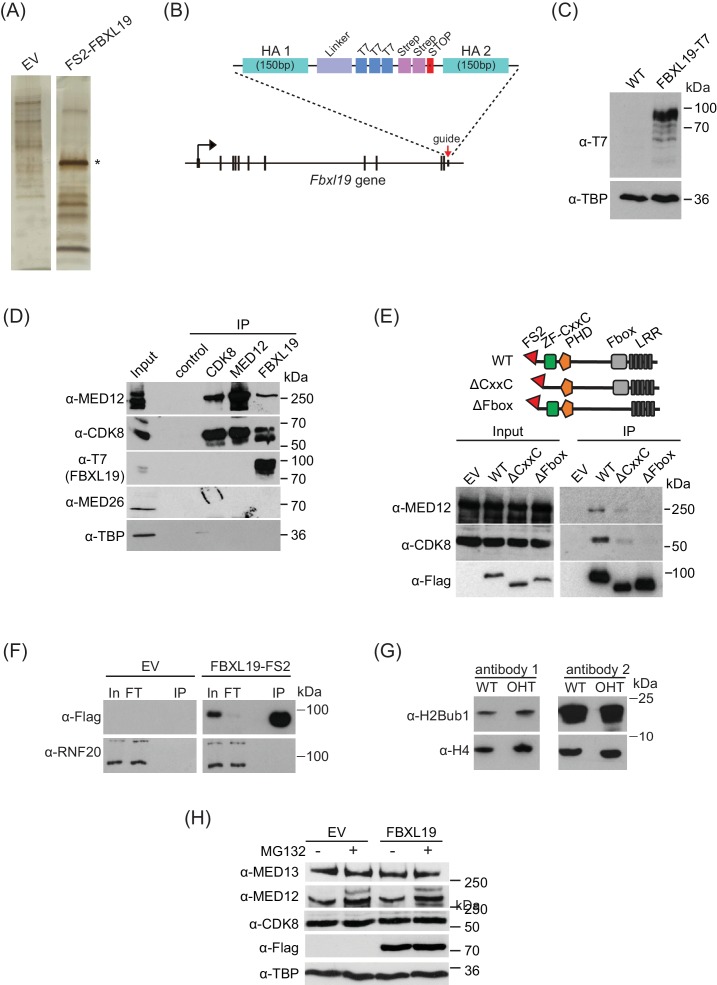
A) A representative silver-stained gel for FS2-FBXL19 purification and an empty vector control (EV) purification. Asterisk identifies the band corresponding to FS2-FBXL19 protein. (
B) In order to visualize FBXL19 protein by western blot in
Figure 2—figure supplement 1D and
Figure 4B, the Fbxl19 gene was tagged by T7 knock-in in
Fbxl19fl/fl ES cells using the CRISPR Cas9 system. A schematic representation of the generation of the C-terminal T7 knock-in Fbxl19 is shown. HA1/2 indicate the homology arms of the targeting construct. (
C) Western blot analysis of the expression of T7-FBXL19 from nuclear extract of the generated T7 knock-in ES cell line. (
D) Western blot analysis of endogenous co-immunoprecipitation (IP) of FBXL19, CDK8 and MED12 from ES cell nuclear extracts. A control IP using a non-specific antibody (α-ΗΑ) was included. (
E) A schematic illustration of the different FS2-FBXL19 truncation mutants and Western blot analysis of purification of FS2-FBXL19 mutants from HEK293T cells probed with the indicated antibodies. (
F) Western blot analysis of FS2-FBXL19 and control purifications (EV) probed with the indicated antibodies. (
G) Western blot analysis of histone extracts generated from
Fbxl19fl/fl (WT) and
Fbxl19ΔCXXC (OHT) ES cells probed with two different antibodies recognizing ubiquitylated H2B K120 (H2Bub1). H4 was used as a loading control. (
H) Western blot analysis of nuclear extracts from HEK293T cells transiently transfected with empty vector (EV) or Flag-FBXL19-expressing vector without (-) or following MG132 treatment (+). Blots were probed with the indicated antibodies. TBP was used as loading control.