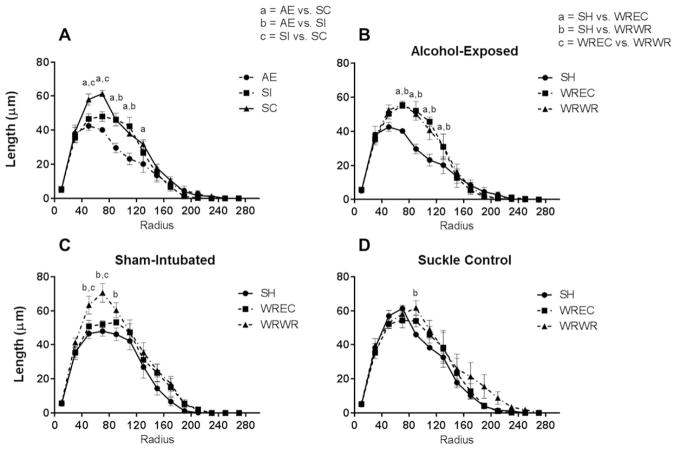
Figure 4.
WRWR and WREC rescue alcohol-induced alterations to amount of dendritic material per radius in the PD72 dorsal dentate gyrus. (A) AE significantly decreased amount of dendritic material per radius in immature dentate granule cells. For this graph, significant differences (p <0.05) at each radii are indicated as a =AE versus SC, b =AE versus SI, and c =SI versus SC. (B) In AE animals, WRWR and WREC ameliorated the negative impact of neonatal alcohol exposure on measures of dendritic length. In graphs B–D, significant differences between housing conditions are indicated as a =SH versus WREC, b =SH versus WRWR, and c =WREC versus WRWR. (C and D) In control animals, WRWR increased dendritic material at certain radii. For SC, WRWR increased dendritic material compared with SH only at 90 μm from the soma. Values indicate means ± SEM.