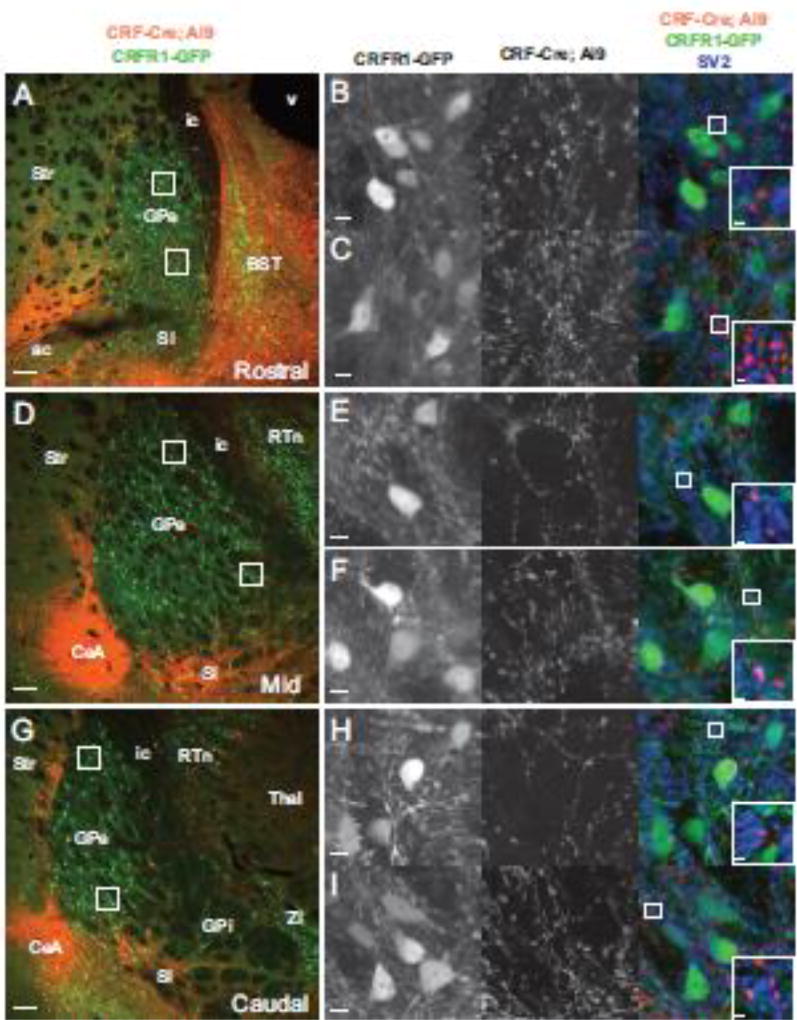
Figure 1. CRF neurons innervate the GPe.
Images of the GPe from mice carrying CRFR1-GFP (green, left column and first column on right), CRF-Cre and a Cre dependent tdTomato reporter (lsl-tdTomato, Ai9, red, left column and second column on right) reveal projections from CRF neurons in close proximity to CRFR1+ neurons. (A) Rostral section at the level of the caudal BST (0.2 mm anterior of bregma). A dorsal closeup (B) and a ventral closeup (C) indicated by boxes in A reveal CRFR1-GFP neurons surrounded by puncta originating from CRF-Cre neurons. The right merged column shows that some of these puncta are positive for the presynaptic marker SV2 (blue), at points of contact between GFP+ dendrites (green) and Tom+ axons (red). (D) A section of the GPe at the level of the amygdala (0.7mm posterior to bregma). Dorsal (E) and ventral (F) closeups show the innervation of CRFR1-GFP neurons by CRF fibers that in some cases are positive for the presynaptic marker SV2. (G) A caudal section of the GPe (1.22mm posterior to bregma). A dorsal (H) and ventral (I) closeup reveal innervation of CRFR1-GFP neurons by CRF neurons. At all three rostro-caudal levels, CRF presynaptic puncta are more dense in the ventral zone compared to the dorsal zone. A, D, G abbreviations: Str - striatum, ic - internal capsule, v - ventricle, ac - anterior commissure, SI - substantia innominata, BST, Bed Nucleus of the Stria terminalis. Scalebars: A, D, G - 100µm, B, C, E, F, H, I - 10µm, insets in right column - 1µm.