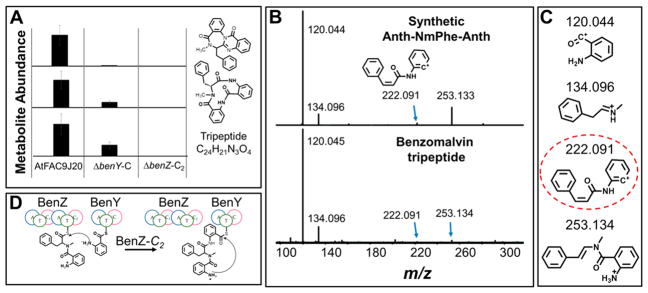
Figure 2.
BenY-C is the CT domain in benzomalvin biosynthesis. (A) The relative abundances of benzomalvin A/D (1), the macrocyclic precursor (2), and the linear tripeptide precursor were determined by LC–MS in AtFAC9J20, AtFAC9J20-ΔbenY-C, and AtFAC9J20-ΔbenZ-C2. The product from AtFAC9J20-ΔbenY-C suggests BenY-C as the CT domain because deletion of an internal C-domain would likely fully block biosynthesis (also see Figure S2). (B) MS2 fragmentation spectrum for the free tripeptide intermediate of benzomalvin biosynthesis compared to that of a synthetic standard of 3, showing the two parent ions share identical fragments, including the diagnostic ion at m/z 222.091 that would not be produced by an Anth-Anth-NmPhe tripeptide. (C) MS2 fragment ions observed in both the synthetic Anth-NmPhe-Anth standard and the benzomalvin linear tripeptide precursor. The dashed circle highlights the diagnostic fragment for the Anth-NmPhe-Anth peptide. (D) Benzomalvin biosynthesis proceeds through a linear Anth-NmPhe-Anth tripeptide intermediate, with BenZ-C2 catalyzing the second peptide condensation.