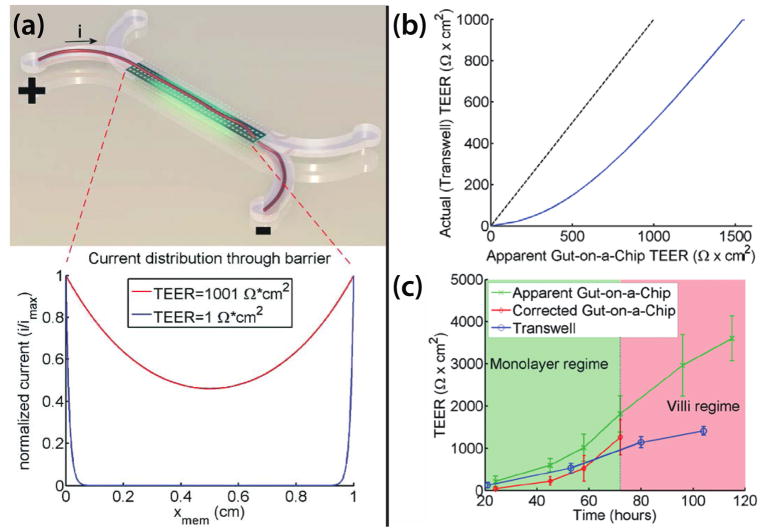
Fig. 9. Comparison of the apparent versus actual TEER in the barrier model of of Odijk et al104.
(a) The distribution of current along the membrane length. Top, artistic rendition of current flow through the membrane. Bottom, the distribution of current flow obtained using an electric circuit analogy. Most currents distribute through the membrane at the beginning and the end of the channel. Since only part of the membranes are conducting currents, the associated voltage drop will be larger, yielding a larger TEER value. (b) Comparison of the actual versus the apparent TEER value. A TEER value is assigned and the apparent TEER value measured on the gut-on-a-chip can be estimated using an electric circuit analogy. (c) Comparison of the corrected TEER value from the gut-on-a-chip versus the TEER value measured from the membrane-insert system, using the same cell line. Based on the correction chart in b, the apparent TEER value measured on the gut-on-a-chip can be corrected to the true TEER value. This correction produced a TEER value that is comparable to the one obtained from the membrane-insert system.