Fig. 1.
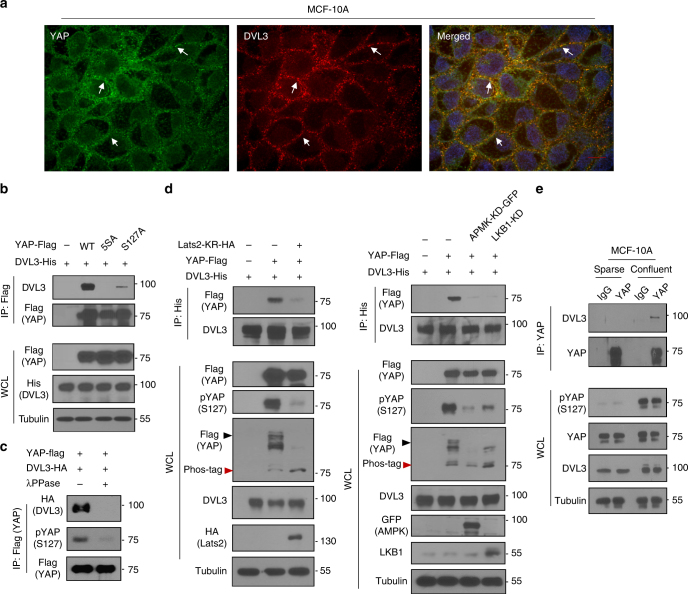
DVL interacts with phosphorylated YAP. a Confocal images of endogenous YAP (green) and DVL3 (red) in MCF-10A cells. Arrows indicate co-localized foci. Nuclear staining with TOPRO3 (blue) is shown in merged image. Scale bar, 10 μm. b DVL interacts with YAP in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. In all, 293 cells were transfected with His-tagged DVL3 and vector control (−) or flag-tagged YAP or mutants (5SA, S127A). Interactions between DVL and YAP were determined following immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-flag antibody and immunoblotting with anti-HA. Whole-cell lysate (WCL) serves as input abundance for IP. c Lambda protein phosphatase (λ PPase) treatment to immunoprecipitated YAP abolishes DVL binding. The 293 cells were transfected with flag-tagged YAP and immunoprecipitated anti-flag beads were treated with λ PPase (+). The agarose beads were then subjected to binding to HA-tagged DVL. d Kinase-dead dominant negative Lats2 (Lats2-KR) or AMPK (AMPK-KD) or LKB1 (LKB1-KD) abolishes YAP and DVL interaction. Flag-tagged YAP and His-tagged DVL3 expression vectors were co-transfected with the dominant negative expression vectors as indicated in 293 cells. Interactions between DVL3 and YAP were determined as described above and phosphorylation status of YAP was determined by pS127-YAP antibody and mobility shift on a phos-tag gel. Black and red arrowheads correspond to the fully phosphorylated and active YAP on a phos-tag gel, respectively. e The MCF-10A cells were cultured under sparse and confluent states, and the whole-cell lysates (WCL) were subjected for immunoblot analysis and immunoprecipitation (IP) assay with anti-YAP antibody. Mouse IgG served as negative control. Unprocessed original scans of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10