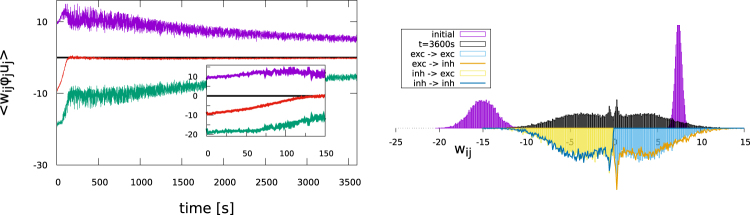
Figure 6.
Left: The evolution of the effective synaptic weights, as for Fig. 4, but for 200 excitatory and 200 inhibitory neurons. The membrane integration time in (1) is set to τ = 20 ms for both excitatory and inhibitory neurons. Synaptic weight balance (7), as expressed by (red curve), is achieved on the time scale 1/εw = 100 s of Hebbian learning (see inset). Note that the initial synaptic weight balance has been selected to be off by a factor of two. Right: The synaptic weight distributions, as for Fig. 5, obtained after one hour of mathematical simulation time. The two small peaks are located at the value for the weight reinserted after pruning. The final distributions are symmetric, apart from some stochastic fluctuations, with standard deviations of 2.7 and means of ±4.1 for excitatory and inhibitory neurons. Note that the initial weight distribution (violet) is highly unbalanced.