Fig. 3.
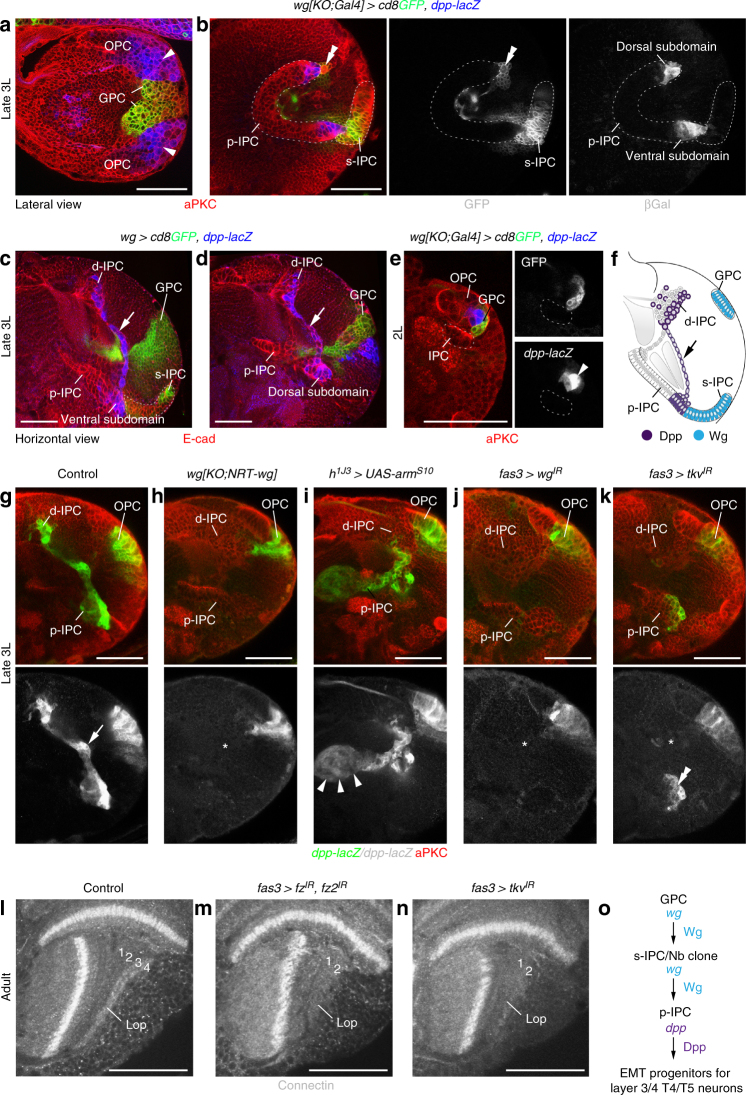
s-IPC-derived Wg is required for Dpp-dependent EMT in the p-IPC. a, b In 3rd instar larvae (3L), dpp-lacZ (blue) was detected in subdomains adjacent to wg{KO;Gal4} UAS-cd8GFP (green) regions in the dorsal and ventral OPC (a, arrowheads) and p-IPC (b). Double arrowhead indicates GFP-positive Nb clone adjacent to the dorsal p-IPC. c, d dpp-lacZ (blue) was maintained in progenitor streams (arrows) from the ventral and dorsal p-IPC subdomains. e In 2nd instar larvae (2L), dpp-lacZ (blue) was present in the OPC (arrowhead) adjacent to wg{KO;Gal4} UAS-cd8GFP-positive GPC areas (green), but was absent in the IPC (dashed line). f Schematic illustrating Wg and Dpp expression domains. Arrow indicates progenitor stream originating from the ventral p-IPC subdomain. g–k Unlike in controls (g, arrow), dpp-lacZ (green) was absent from the IPC in wg{KO;NRT-wg} flies (h, asterisk). The OPC was not affected. dpp-lacZ was ectopically induced in the IPC (arrowheads) by h1J3-Gal4-mediated expression of UAS-armS10 (i). dpp-lacZ was absent following fas3NP1233-Gal4-mediated IPC-specific wg knockdown. In the Dpp-expression domain, this caused EMT defects and loss of progenitor streams (j, asterisks). Similar defects were caused by IPC-specific tkv knockdown. dpp-lacZ remains expressed in the p-IPC (k, double arrowheads). l–n Compared to controls (l), fas3NP1233-Gal4-mediated IPC-specific knockdown of fz and fz2 (m) and tkv (n) caused the loss of lobula plate (Lop) layers 3/4 labeled with Connectin in adults. o Summary of wg and dpp function in the GPC areas, the s-IPC/Nb clone, and p-IPC. For genotypes and sample numbers, see Supplementary Table 1. Scale bars, 50 μm