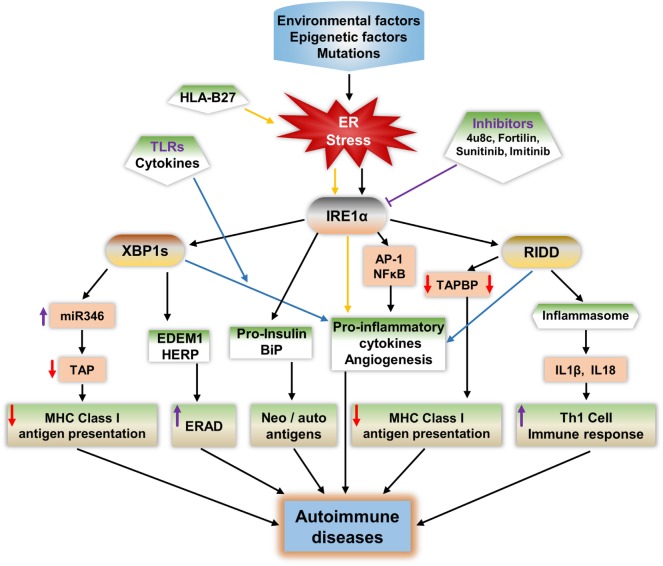
Figure 3.
Potential mechanisms of IRE1α in the development of autoimmune diseases. IRE1α activation by environmental factors or gene mutations that induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress can lead to autoimmune disease development through various pathways. Spliced XBP1s increases the expression of the microRNA miR-346, which binds to the 3′-UTR of transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) mRNA, leading to TAP mRNA decay. This reduces MHC class I complex formation and antigen presentation. XBP1s increases the expression of ER degradation-enhancing α-mannosidase-like protein and homocysteine-induced ER protein, leading to enhanced ER-associated degradation (ERAD), which can lead to autoimmune disease by increasing immune cell survival especially that of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Misfolded proteins may act as autoantigens; for example, human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27), immunoglobulin binding protein (BiP), and pro-insulin. IRE1α has a role in the increased expression of BiP, and pro-insulin during stress and these proteins may act as autoantigens/neoantigens. IRE1α activation during the response to misfolded HLA-B27 misfolded response may contribute to autoimmunity in ankylosing spondylitis. ER stress or toll-like receptor-activated IRE1α mediates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines through c-Jun N-terminal kinase, such as NFκB, XBP1s, and regulated IRE1α-dependent decay (RIDD), which increases the pathogenesis in autoimmune diseases. RIDD activity reduces MHC class I antigen presentation by reducing TAPBP protein synthesis. In addition, RIDD-mediated activation of nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, and pyrin domain-containing-3 inflammasomes leads to increased secretion of IL-1β and IL-18, which increase the T-helper-1 cell immune response, which is characteristic of many autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, through inhibition of IRE1α, either with small chemical molecules, such as 8-formyl-7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin (4μ8c), sunitinib, imatinib, or by enhancing expression of negative regulators of IRE1α such as fortilin, it may be possible to reduce the progression of autoimmune diseases.