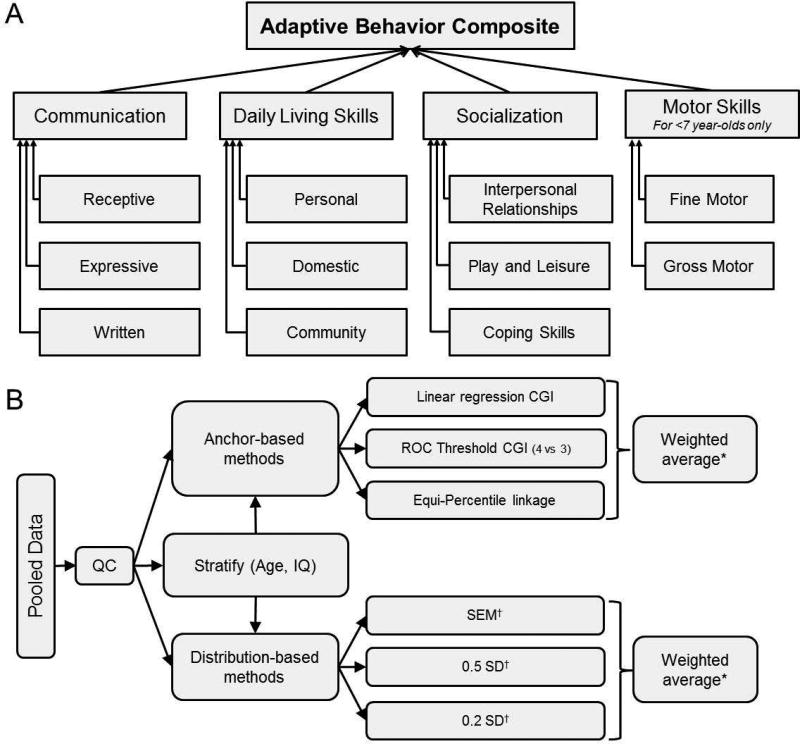
Figure 1.
Structure of the Vineland-II and of the analysis strategy for estimating the MCID. A. The Vineland-II assesses 11 subdomains of adaptive behavior grouped into four domains; sums of these scores are standardized into Communication, Daily Living Skills, Socialization and Motor Skills domain standard scores. Sums of the domain standard scores are then standardized into the Adaptive Behavior Composite score. B. Individual-level data was pooled across multiple consortia, trials and registries, and subjected to several quality control steps. Next, both anchor-based and distribution-based techniques for estimating the MCID were performed on the entire pooled dataset, as well as stratified subsets of the pooled dataset. *Sample-size weighting is used, such that the number of individuals contributing to each anchor- or distribution-based estimate is directly proportional to the influence of that estimate on the weighted-average; †Both cross-sectional and longitudinal assessments were performed.