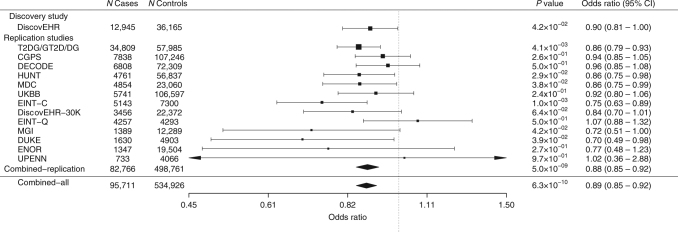
Fig. 1.
ANGPTL4 p.E40K associates with reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. The association between the p.E40K variant and type 2 diabetes was tested in each study using logistic or Firth logistic regression, coding genotypes according to an additive model. “Combined” effects were calculated using inverse variance weighted fixed-effects meta-analysis. For each study, the squares indicate the odds ratio and lines indicate 95% confidence intervals. The square size is proportional to the standard error of the estimate. CI confidence interval, CGPS Copenhagen General Population Studies, DECODE deCODE, DiscovEHR DiscovEHR Discovery Study, DiscovEHR DiscovEHR-30K, DiscovEHR 30K Replication Study, EINT-C EPIC interact–CoreExome, EINT-Q EPIC Interact–Quad660, ENOR EPIC Norfolk, HUNT the Nord-Trøndelag Health study, MDC Malmo Diet and Cancer Study, MGI the Michigan Genomics Initiative, TD2G/GT2D/DG combined analysis of T2D-GENES, GoT2D, and DIAGRAM studies, UKBB United Kingdom Biobank. The study populations are described in full in Supplementary Table 4 and in the Supplementary Note