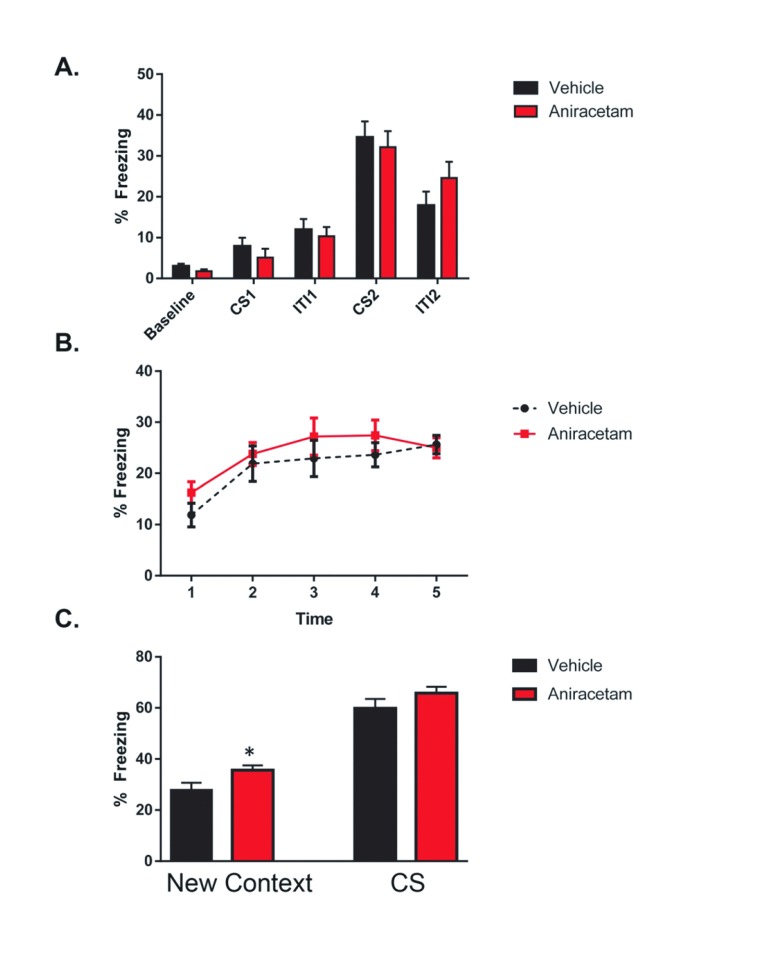
Figure 5. Aniracetam pretreatment does not change performance on the delayed fear conditioning task.
( A) On the first day of testing, mice were placed into the operant chamber and 2 minutes of baseline activity levels were recorded. This was followed by a 30 second conditioned stimulus (CS) tone (80dB white noise), a 2 second unconditioned stimulus (US) shock (0.85mA), and a 2-minute inter-trial interval (ITI). Another identical CS-US pairing was then presented and followed with a 30 second ITI. Following multiple foot shock and tone presentations, a two-way ANOVA test indicated no main effect of group (F (1, 19) = 0.1048; p = 0.7497) or interaction between groups (F (4, 76) = 0.5453; p = 0.7029). ( B) The second day of testing consisted of two trials. During the first trial, mice were placed back into the original operant chamber for 5 minutes and baseline activity was recorded. ( C) Before the second trial the operant chamber was modified with a foam pad under an acrylic square to cover the metal floor grid, an acrylic wall placed diagonally across that halved the space into triangular form, and 1mL of pure vanilla extract (Adam’s Extracts, USA) placed beneath the floor. These changes to the tactile, spatial, and olfactory contexts of the chamber were made in order to prevent context dependent learning. During the second trial, mice were placed into the contextually modified operant chamber and 3 minutes of the trial baseline activity was monitored. Aniracetam mice displayed significantly increased freezing in the novel context t(1,22) = 2.984, p = 0.004. This was followed by a 3-minute period of CS tone presentation (80dB white noise). There was no significant difference in the freezing behavior expressed between treated and control mice t(1,22) = 1.976, p = 0.052.