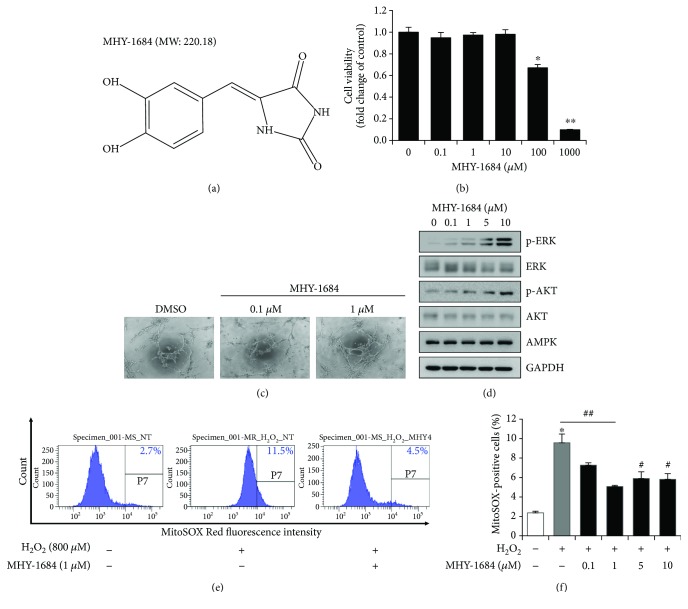
Figure 1.
The role of MHY-1684 as an ROS scavenger in hCPCs. (a) The chemical structure of MHY-1684. (b) hCPCs were seeded in 96-well plates and cultured with the indicated concentrations of MHY-1684 for 24 h. Cell viability was assessed using the WST assay. Values are the mean ± S.E.M. ∗ p < 0.05 and ∗∗ p < 0.01 as compared with the control group. (c) The tube-forming ability of hCPCs was examined when cells were exposed to MHY-1684 for 24 h. The tubular-like network was evaluated using a Matrigel tube formation assay. (d) After treatment with MHY-1684 for 24 h, the prosurvival-related proteins (ERK-1, AKT-1) were analyzed by Western blotting. (e) hCPCs were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of MHY-1684 for 24 h prior to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 800 μM) treatment. Mitochondrial ROS levels in hCPCs were measured by flow cytometry with MitoSOX Red. (f) Histogram indicates median value ± S.E.M. of MitoSOX-positive cells when exposed to H2O2. MitoSOX-positive cells increased when exposed to H2O2; however, when cotreated with MHY-1684, the MitoSOX-positive cells decreased significantly. Values are the mean ± S.E.M. ∗ p < 0.05 and ∗∗ p < 0.01 as compared with the control group; # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 as compared with the group treated with 25 mM D-(+) glucose for 72 h.