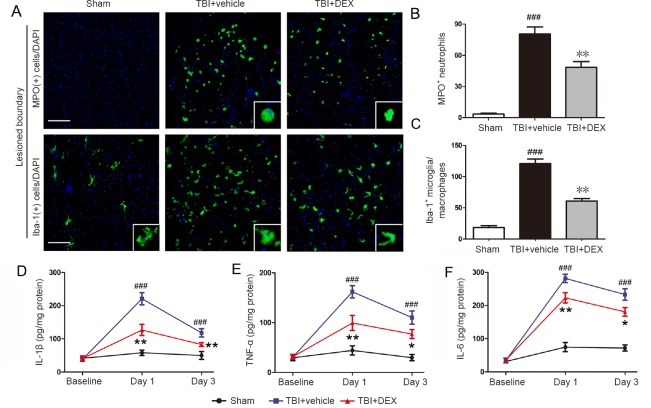
Figure 2.
Effect of dexmedetomidine (DEX) on neutrophil infiltration, microglial activation, and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion following traumatic brain injury (TBI).
(A–C) Representative immunofluorescence photomicrographs (A) and quantitative data for myeloperoxidase (MPO)-positive neutrophils on day 1 (B) and ionized calcium binding adapter molecule-1 (Iba-1)-positive microglia on day 3 (C) in the lesioned boundary post-injury (n = 5 per group at each time point). Scale bars: 200 μm. Inset shows positive cells at a high magnification. (D–F) enzyme linked immunosorbent assay results showing the concentration of interleukin-1β (IL-1β; D), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α; E), and IL-6 (F) in the lesioned cerebral cortex on days 1 and 3 post-injury (n = 5 per group). All data are expressed as the mean ± SD, and were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc test. ###P < 0.001, vs. sham group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. TBI + vehicle group.