Figure 2.
Depletion of JMJD1A and JMJD1B Induces Growth Arrest in ESCs
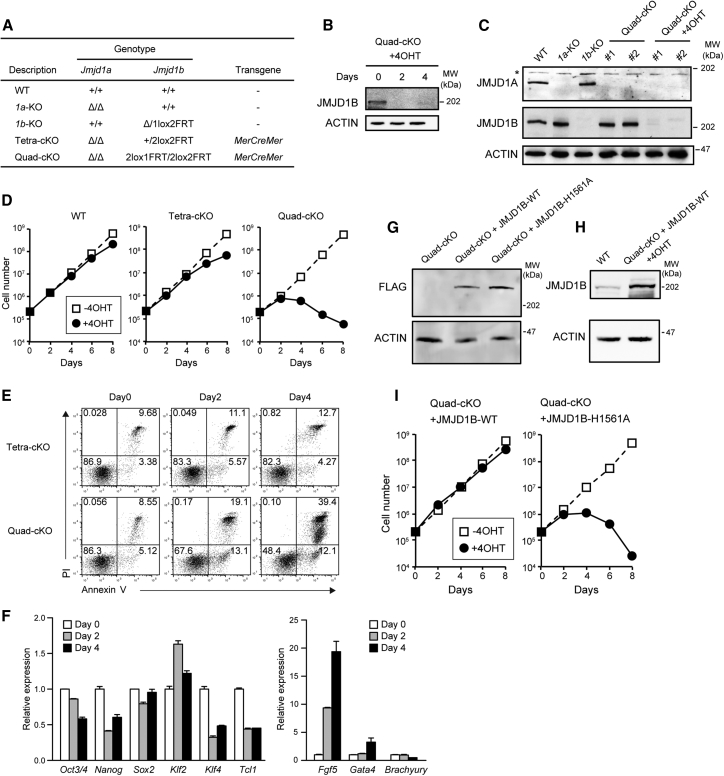
(A) List of the established ESC lines and their genotypes. MerCreMer, Cre flanked by mutated estrogen receptor ligand-binding domains.
(B) Time-course analysis of 4OHT-dependent depletion of JMJD1B in Quad-cKO cells.
(C) Immunoblot analyses of JMJD1A/JMJD1B-depleted ESC lines. Whole extracts of the indicated ESC lines were fractionated using SDS-PAGE and then applied to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against JMJD1A and JMJD1B. JMJD1A and JMJD1B were depleted in the Quad-cKO cell lines cultured with 800 nM 4OHT for 4 days. Asterisk (∗) represents non-specific signals.
(D) The indicated ESC lines were cultured in the presence or absence of 4OHT. Cell numbers were determined every 2 days. Growth arrest became apparent when the Quad-cKO cell line was cultured in the presence of 4OHT for 4 days (right). In contrast, wild-type (left) and Tetra-cKO (middle) cells grew in the presence of OHT.
(E) Time-course analysis of JMJD1 depletion-induced cell death. The indicated ESC lines were cultured in the presence of 4OHT, following which the cells were stained with PI and annexin V and analyzed using flow cytometry.
(F) Expression levels of pluripotency-associated (left) and lineage-associated (right) genes in Quad-cKO cells treated with 4OHT were examined using RT-qPCR. We used Fgf5, Gata4, and Brachyury as the markers for primitive ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm, respectively. Representative data are presented from independent triplicate experiments. Error bars indicate means ± SD derived from technical replicates.
(G and H) Rescue of the growth arrest phenotype by exogenous introduction of JMJD1B into Quad-cKO cell line. (G) Expression vectors for FLAG-tagged wild-type JMJD1B or enzymatically inactive H1561A mutants of JMJD1B were individually and stably introduced into the Quad-cKO cell line. The expression levels of exogenously expressed proteins were compared by immunoblot analysis. (H) Comparison of protein expression levels of endogenously expressed JMJD1B and exogenously expressed JMJD1B using anti-JMJD1B antibody. JMJD1B expression levels were compared between wild-type ESCs and 4OHT-treated Quad-cKO cells expressing FLAG-JMJD1B-WT.
(I) Quad-cKO cell lines expressing wild-type JMJD1B (left) or the enzymatically inactive H1561A mutant of JMJD1B (right) were cultured in the presence of 4OHT. Exogenous expression of wild-type JMJD1B rescued the growth arrest phenotype of Quad-cKO cells in the presence of 4OHT, whereas the enzymatically inactive H1561A mutant did not.