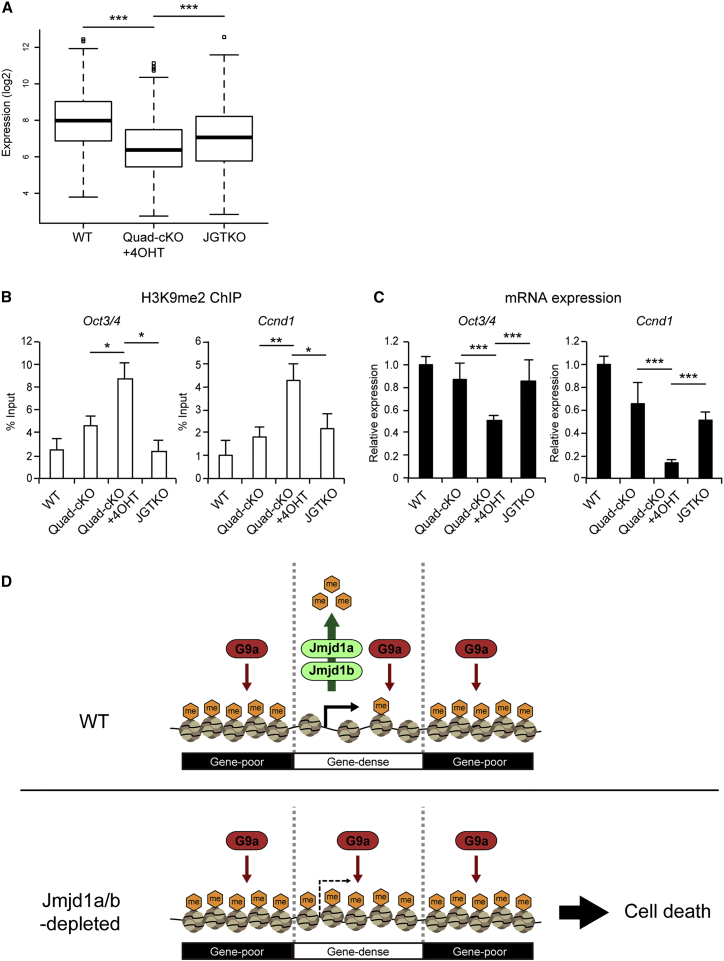
Figure 7.
G9a Mutation Rescues JMJD1A/JMJD1B-Depletion-Induced Transcriptional Downregulation
(A) Comparison of average expression levels of 204 genes that were downregulated by JMJD1A/JMJD1B depletion between the mutant ESCs. Introduction of G9a mutation in JMJD1A/JMJD1B-deficient background significantly restored the expression levels of those genes. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student's t test).
(B and C) JMJD1A/JMJD1B and G9A antagonistically tune the H3K9 methylation levels of Oct3/4 and Ccnd1 to ensure accurate transcription. (B) The H3K9me2 levels in the promoter regions of Oct3/4 (left) and Ccnd1 (right) were examined by performing ChIP-qPCR analyses. Increased H3K9me2 levels in these genes in JMJD1A/JMJD1B-double-depleted cells were rescued by G9A depletion. (C) The expression levels of Oct3/4 (left) and Ccnd1 (right) were examined by RT-qPCR analyses. Reduced expression levels of these genes in JMJD1A/JMJD1B-double-depleted cells were rescued by G9A depletion. mRNA expression levels of wild-type cells were defined as 1. For (B) and (C), data are presented as means ± SD. n = 3 independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student's t test).
(D) Schematic representation of the roles of JMJD1A/JMJD1B in ESCs. JMJD1A/JMJD1B ensure cell viability and transcriptional accuracy by antagonizing G9a-mediated H3K9 overmethylation in gene-rich euchromatin in ESCs. In wild-type ESCs, JMJD1A/JMJD1B preferentially remove H3K9 methylation marks from gene-rich euchromatin. The compound loss of JMJD1A/JMJD1B results in G9a-mediated H3K9 overmethylation in euchromatin, thereby inducing cell death and impaired gene expression.