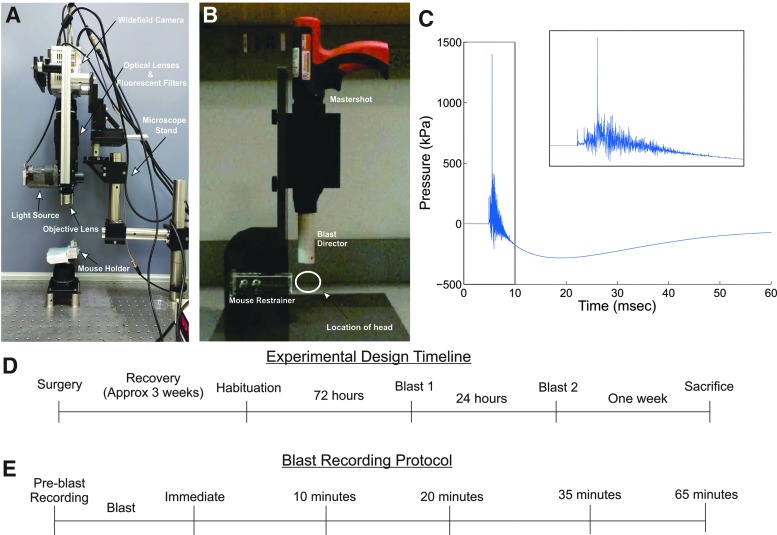
FIG. 1.
Experimental design for wide-field Ca2+ imaging of hippocampal neurons in mice exposed to a cranial blast (A) A wide-field fluorescence microscope coupled to a scientific complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (sCMOS) camera was used to image neurons expressing a genetically encoded Ca2+ sensor (GCaMP6f) in vivo. (B) The Cranium Only Blast Injury Apparatus (COBIA) consisted of a modified nail gun coupled to a blast director to direct the blast wave vertically onto the freely moving head of unanesthetized mice. The distance from the animal's head to the opening of the blast director was 2 cm. (C) Waveform of average overpressures (n = 5 tests) generated from the COBIA. Inset shows the zoom in of the waveform over 10 ms. (D) Experimental timeline. (E) Ca2+ imaging protocol during each blast session.