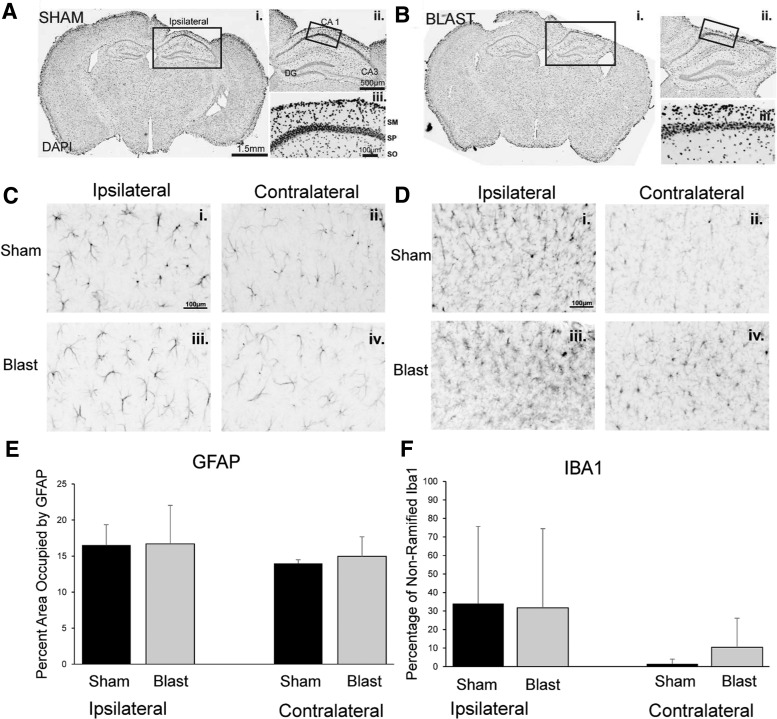
FIG. 6.
No significant differences in glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ionized Ca2+ binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1) immunoreactivity following blasts. (A, B) 4′6-diamindino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) labeled coronal sections from a representative sham-exposed mouse (Ai.-iii.) and a representative blasted mouse (Bi.-iii.). DAPI = 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole. GFAP = glial fibrillary acidic protein. CA1, Cornu Ammonis 1; SM, stratum moleculare; SP, stratum pyramidale. SO, stratum oriens. (C,D) GFAP immunofluorescence (C) and Iba1 immunofluorescence (D) from a sham mouse (top) and a blast exposed mouse (bottom), ipsilateral (i., iii.) and contralateral to the imaging window (ii., iv.). (E) No significant difference in the percent area of GFAP immunofluorescence was observed between sham and blast exposed animals, either ipsilateral or contralateral to the imaging window. (F) No significant difference in the percentage of unramified cells positive for Iba1 was observed between sham and blast exposed animals ipsilateral or contralateral to the imaging window.