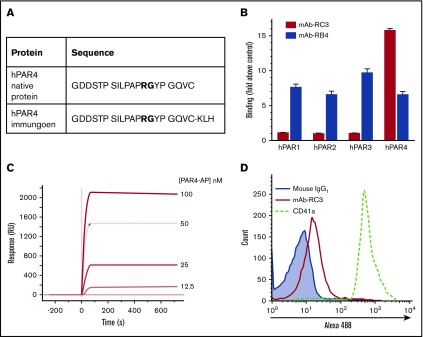
Figure 1.
Development of a human monoclonal function-blocking antibody against human PAR4. (A) HumAb mice were immunized with a KLH-coupled peptide corresponding to a region in the N-terminus of hPAR4 spanning the thrombin cleavage site (GDDSTPSILPAPRGYPGQVC-KLH; bold font indicates thrombin cleavage site). (B) Initial ELISA-based antigen screening showed clone mAb-RC3-bound native human PAR4 peptide (hPAR4) with a 16-fold selectivity over human PAR1, PAR2, or PAR3 peptides; another clone (mAb-RB4) bound all 4 peptides similarly. Note the lack of binding of mAb-5RC3 to any of hPAR1, hPAR2, or hPAR3 peptides above control (media only). (C) Binding was confirmed by surface plasmon resonance analysis, which showed that mAb-RC3 bound native PAR4 peptide with a KD ∼0.4 nM. (D) mAb-RC3 (10 μg/mL) binding to human PAR4 on the platelet surface was confirmed by flow cytometry. Data are mean ± standard error of the mean in panel B and are representative traces (C-D) of n = 3 independent experiments.