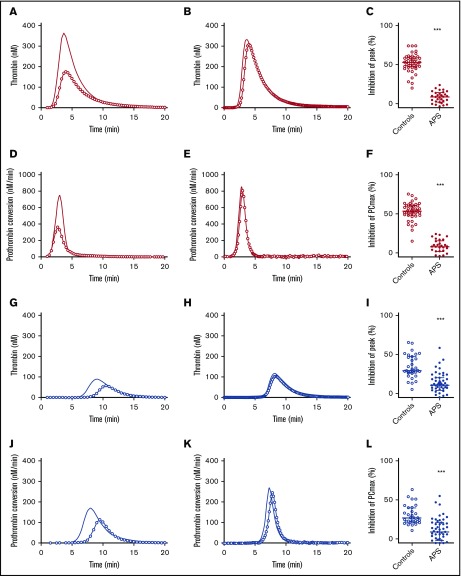
Figure 4.
Thrombomodulin sensitivity of TG and thrombin dynamics in healthy subjects and APS patients with (blue) or without VKA treatment (red). (A-C) The inhibition of TG (continuous line) by 20 nM TM (line with circle symbols) was measured in healthy controls (A) and APS patients without VKAs (B). The effect of TM was quantified as the percentage inhibition of TG peak height (C). (D-F) The inhibition of prothrombin conversion (continuous line) by 20 nM TM (line with circle symbols) was measured in healthy controls (D) and APS patients without VKAs (E). The effect of TM was quantified as the percentage inhibition of PCmax (F). (G-I) The inhibition of TG (continuous line) by 20 nM TM (line with circle symbols) was measured in controls on VKA (G) and APS patients on VKAs (H). The effect of TM was quantified as the percentage inhibition of TG peak height (I). (J-L) The inhibition of prothrombin conversion (continuous line) by 20 nM TM (line with circle symbols) was measured in controls on VKA (J) and APS patients on VKAs (K). The effect of TM was quantified as the percentage inhibition of PCmax (L). ***P < .001 compared with the control group using a 2-sided Mann-Whitney U test.