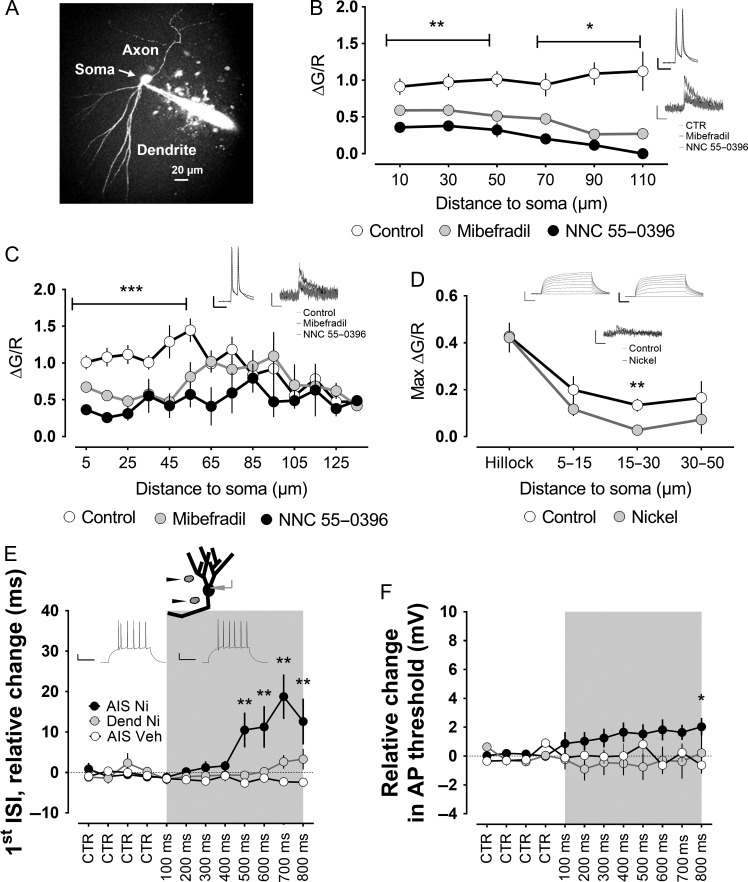
Figure 3.
T-type channels at the level of the axon initial segment mediate burst firing of mature granule cells. (A) Two-photon fluorescent image of a mature granule cell filled with Alexa594, as a volume marker, and the calcium indicator Fluo-5F. (B) The cells received short pulses of current injection to the soma to evoke a doublet of action potentials at 50 Hz, as shown in the inset. T-type channel blockers mibefradil and NNC-55 0396 caused a significant reduction in the doublet-evoked calcium influx all along the recorded dendrites. In the axon, however, the effect was stronger in the proximal part (C). Insets show examples of electrophysiological and calcium influx traces in the corresponding groups for the proximal axon and dendrite. Scale bars: 20 mV/50 ms, 0.5 dG/R/500 ms. (D) To further understand the spatial distribution of the T-type-mediated calcium influx into the proximal axon, we blocked action potentials with TTX and used a longer current injection similar to the one used in a previous series of experiments. A significant effect of the T-type channel blocker nickel was only verified at a distance of 15–30 μm from the soma. Insets show examples of electrophysiological and calcium influx traces. Scale bars: 20 mV/50 ms, 0.5 dG/R/500 ms. (E) Nickel or vehicle solution was puffed at dendrites or the axon initial segment, as indicated. For each cell, 4 repeats were taken as the baseline (CTR), and puffs of increasing duration, from 100 up to 800 ms, were then applied at the specified locations. Applying nickel locally to dendrites did not significantly modify the bursting, quantified as the first ISI. In addition, there was no significant effect of local application of vehicle solution to the axon initial segment of mature granule cells. However, puffing nickel at the axon initial segment produced a highly significant increase in the first ISI. The traces in the inset show the pattern of action potentials in the control condition (left) or when puffing nickel to the AIS (right). Scale bars: 20 mV/100 ms. (F) In addition to the strong effect on the burst firing, the puff of nickel at the axon initial segment also slightly increased the threshold of the action potential, although it only reached statistical significance for the longest puff. *,**, ***P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.001, Mann–Whitney U-test.