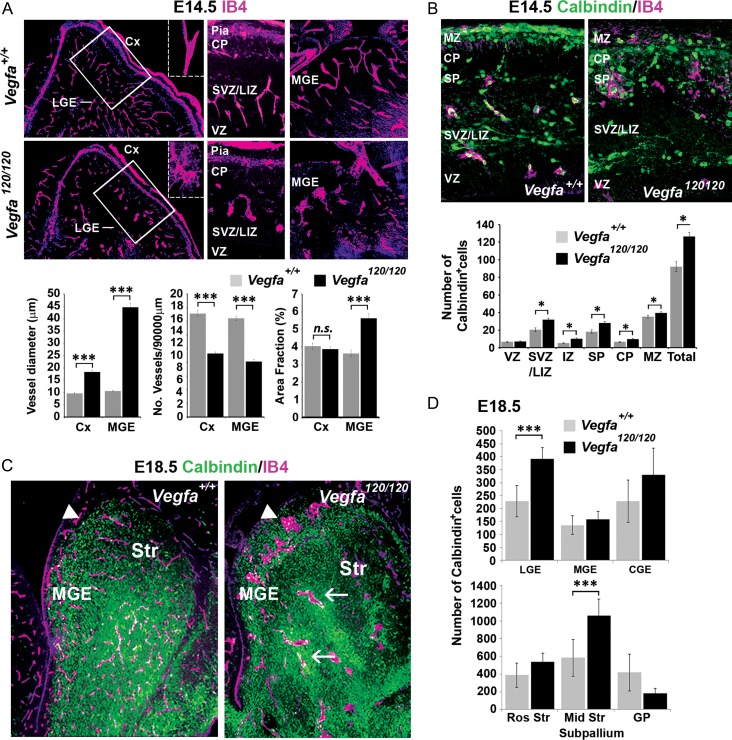
Figure 4.
Interneurons tangential migration to the cortex is impeded at late but not mid phases of development in the Vegfa120/120 mutant forebrain with a defective vascular network. (A) IB4+ labeling of blood vessels in coronal sections of E14.5 Vegfa+/+ wildtype and Vegfa120/120 knock-in mouse forebrain; with vessel diameter, number and area fraction occupancy quantified in bar charts. (***P ≤ 0.0001, t-test; n = 4 for each). (B) IB4+ labeling of blood vessels and immunolocalization of Calbindin+ interneurons in coronal sections of E14.5 Vegfa+/+ wildtype and Vegfa120/120 knock-in mouse forebrain, with mean number of interneurons represented in bar charts. (*P ≤ 0.05; t-test; n = 3 for each). (C) IB4+ labeling of blood vessels and immunolocalization of Calbindin+ interneurons in the coronal sections through the subpallium of E18.5 VegfA+/+ and VegfA120/120 mouse forebrains. Arrows show accumulation of interneurons adjacent to dilated blood vessels. (Data in all graphs represent values ±SEM). (D) Mean number of Calbindin+ cells quantified in subpallial regions shown by bar charts. LGE, lateral ganglionic eminence; Cx, cortex; CP, cortical plate; SP, subplate; IZ, intermediate zone; IZ/SVZ, lower intermediate zone/subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone.