Figure 2.
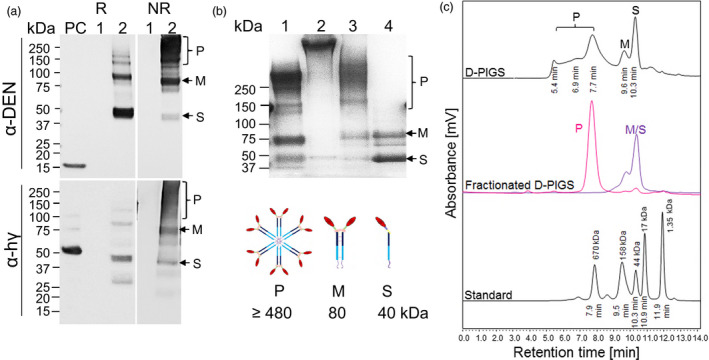
Expression, purification and molecular fractionation of dengue poly‐immunoglobulin G scaffold (D‐PIGS). (a) D‐PIGS were expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana plants and the extracts analysed by Western blotting under reducing (R) or nonreducing (NR) conditions using antidengue or anti‐Fc gamma antibodies. ‘PC’ is the positive control (recombinant cEDIII or human IgG1, respectively). Lane 1: wild‐type plant extract; lane 2: unfractionated D‐PIGS. Positions of the single chain (S), monomer (M) and polymers (P) are indicated. (b) SDS‐PAGE and Commassie staining of fractionated D‐PIGS. Lanes: 1. Commercial (Sigma) human sIgA; 2. Commercial (Sigma) human IgM; 3. Polymers and 4. Monomers. The schematics bellow indicate the expected molecular sizes for each fraction. (c) HPLC profile of D‐PIGS. Unfractionated (upper panel) and fractionated (middle panel) D‐PIGS. Indicated retention times were used to estimate the molecular weights of each fraction, based on gel filtration protein standards (bottom panel). The fractionated D‐PIGS were used in immunogenicity studies with tonsillar cultures (Figure 1b).
