Figure 3.
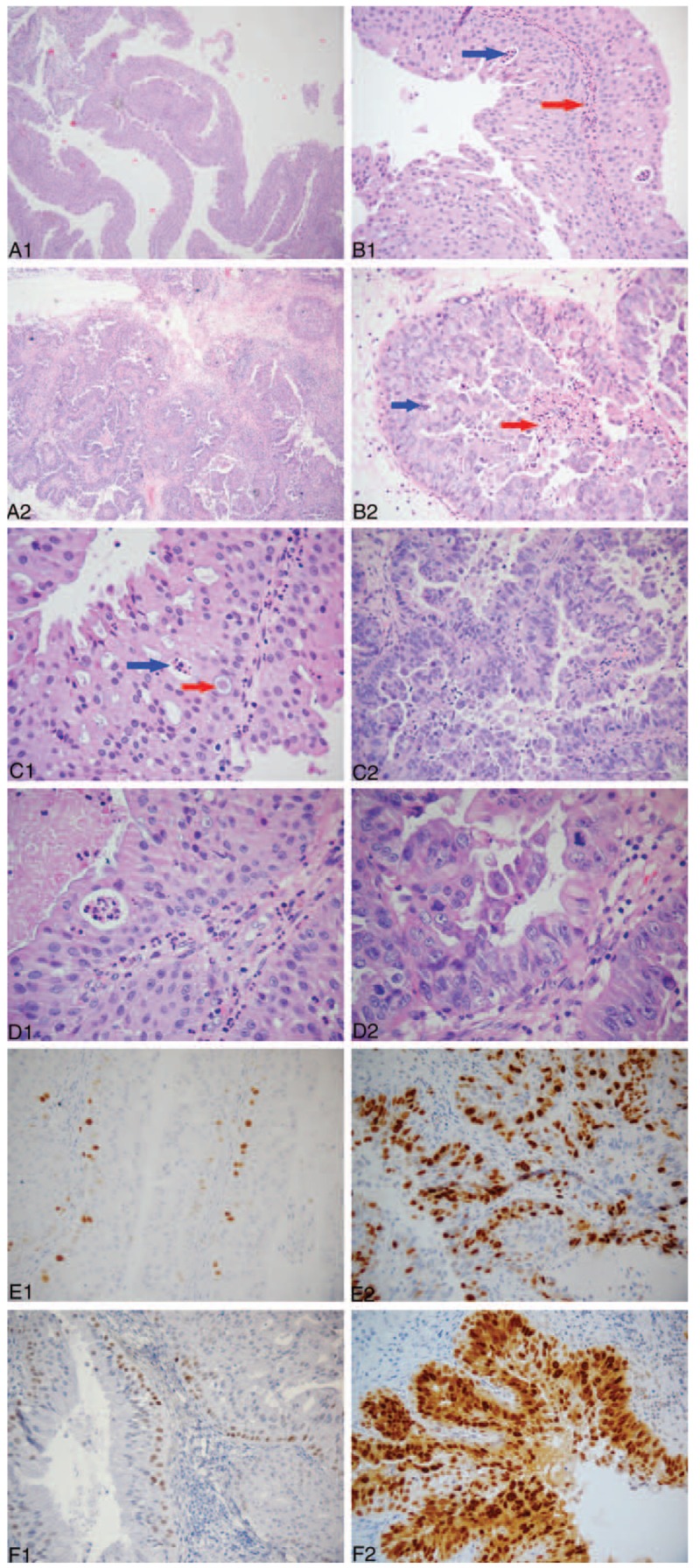
Pathological characteristics and immunohistochemical findings in the tumor in the second surgery. (A1) Low-power view showing the predominantly papillary surface pattern of the tumor. The cells are acidic. (B1) Medium-power view showing the microabscess structure of neutrophils with neatly arranged cells and no atypia. The blue arrow shows a microabscess and the red arrow indicates fibrous vascular axis. (C1) Scattered mucous cells and small cavities were visible under high-power view, and the cells were not heterotypic. The blue arrow shows a microabscess and the red arrow indicates a mucous cell. (D1) The structure is clearer under higher magnification. (E1) Ki67 staining of the tumor specimen. The proliferation index is low and only the basal layer cells are positive, indicating that the growth of the tumor is slow. (F1) p53 staining of the tumor specimen. Only the basal layer cells were positive, but the surface cells were negative, indicating that the cells were benign. Additional pathological characteristics and immunohistochemical findings in the tumor in the second surgery. (A2) Low-power view showing the predominantly papillary surface pattern of the tumor. Part of the tumor shows formation of small clusters, with crowded cells and the layered structure disappears. Visible infiltration of gland tubular structure in the stroma. (B2) Medium-power view showing glandular fusion, obvious cell atypia and visible nucleolus. The blue arrow shows a pathological mitosis-like nucleus, and the red arrow indicates necrosis/nuclear fragmentation. (C2) High-power view showing that the cells were crowded, disordered and heterotypic. (D2) Higher magnification of the mitotic-like nucleus. (E2) Ki67 staining indicated a high proliferation index. (F2) p53 staining of the tumor cells was positive, suggesting cell malignancy.
