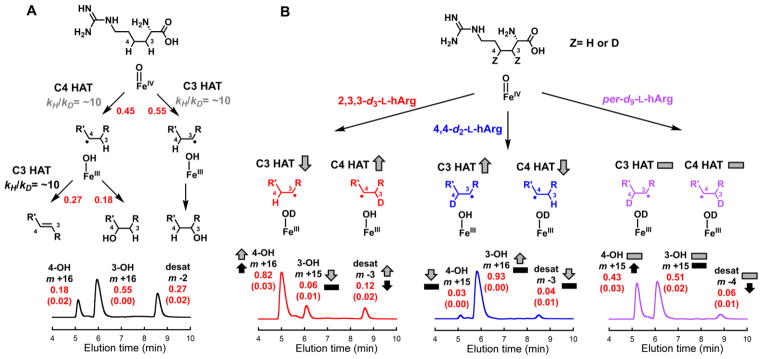
Figure 7.
LC-MS analysis of the transformations of L-hArg deuterium isotopologs by VioC, and interpretation of the results in terms of mechanistic pathways, 2H-KIE (kH/kD) values, and impacts on partition ratios. A, All-protium L-hArg. B, C3-labeled L-Arg (red), C4-labeled L-Arg (blue), and uniformly labeled L-Arg (purple). The red values are partition ratios for (i) the initial HAT to the ferryl complex from C3 or C4 (upper in A), (ii) the fate of the C3 radical, rebound or second HAT (middle in A), and (iii) overall products (lower in A and B). The red numbers in parentheses are the standard deviations of the values from three independent trials. The 2H-KIE values that rationalize the impacts of deuterium substitution on the partition ratios are shown in gray and black (in A). The arrows and dashes (in B) illustrate the qualitative impacts of the 2H-KIEs on the partitions between HAT from C3 or C4 to the ferryl complex (gray), between the two pathways for decay of the C3 radical (black), and among the three possible products (gray and black). Details of the analytical procedure are provided in the Supporting Information. The values resulting from product detection by A260 (from the Fmoc group) are compared in Table S3.