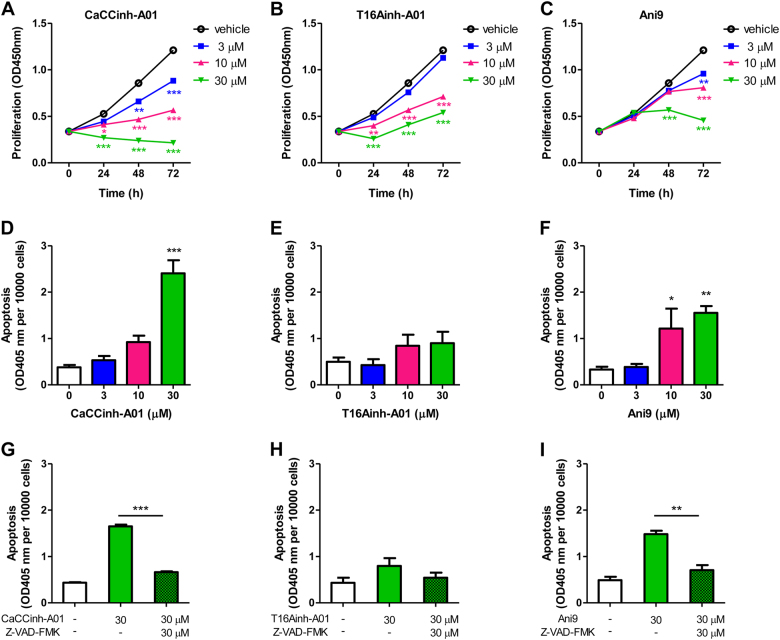
Fig. 3. Pharmacological inhibition of ANO1 decreases cell growth and induces apoptosis in PC-3 cells.
a–c PC-3 cells were treated with different concentrations of ANO1 inhibitors CaCCinh-A01 (a), T16Ainh-A01 (b), or Ani9 (c) in 0.5% FBS medium. Cell proliferation was measured by CCK-8 assay. Data are presented as the means ± SEM; n = 6. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs vehicle (0.1% DMSO). Inhibition of ANO1 with CaCCinh-A01, T16Ainh-A01, or Ani9 decrease viable cell number in a dose-dependent or time-dependent manner. d–f Bar graphs showing apoptosis of PC-3 cells after 72 h inhibition of ANO1 with CaCCinh-A01 (d), T16Ainh-A01 (e), or Ani9 (f) (means ± SEM; n = 4). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs vehicle (0.1% DMSO). CaCCinh-A01 and Ani9 markedly induce apoptosis in a good dose-dependent manner whereas T16Ainh-A01 shows the weak effect. g–i Z-VAD-FMK, a pan-caspase inhibitor, blocks apoptosis induced by CaCCinh-A01 and Ani9. PC-3 cells were treated with CaCCinh-A01 (g), T16Ainh-A01 (h), or Ani9 (i) and co-treated with 30 μM of Z-VAD-FMK for 72 h. Data are expressed as the means ± SEM (n = 4). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for statistical significance and comparisons between Z-VAD-FMK versus vehicle groups