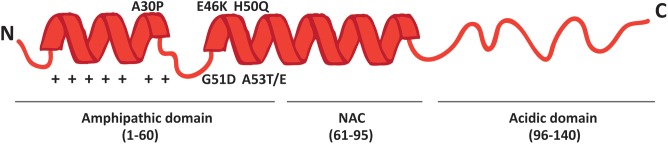
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of α-syn structure. The protein forms two alpha-helices when interacting with lipids and is composed of three distinct domains: the N-terminal amphipathic region, the non-amyloidogenic component (NAC) and the C-terminal acidic domain. The N-terminal domain drives α-syn to mitochondria thanks to the presence of seven positively charged lysine residues (indicated as +) and contains all the PD-related mutations.