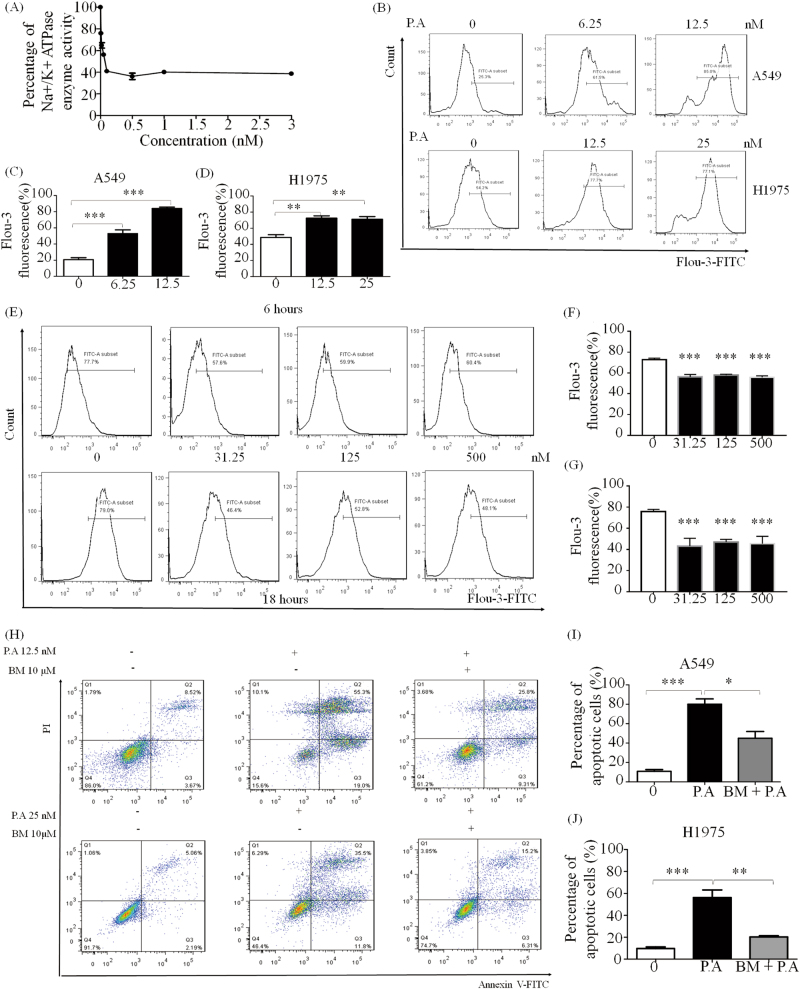
Fig. 3. P.A inhibited Na+/K+ ATPase and regulated [Ca2+] levels in NSCLC.
a P.A significantly inhibited Na+/K+ ATPase, and its IC50 was measured by in vitro Na+/K+ ATPase assay; b P.A elevated [Ca2+] levels after 6 h of treatment in A549 and H1975 cells; c, d Statistical results of b (three independent experiments); e P.A decreased [Ca2+] levels after 6 and 18 h treatment in CCD19-LU; f, g Statistical results of e (three independent experiments); h Increased intracellular [Ca2+] levels were required for P.A-induced apoptosis. A calcium chelator (BM) remarkably inhibited P.A-induced apoptosis; i, j Statistical results of e (three independent experiments) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001)