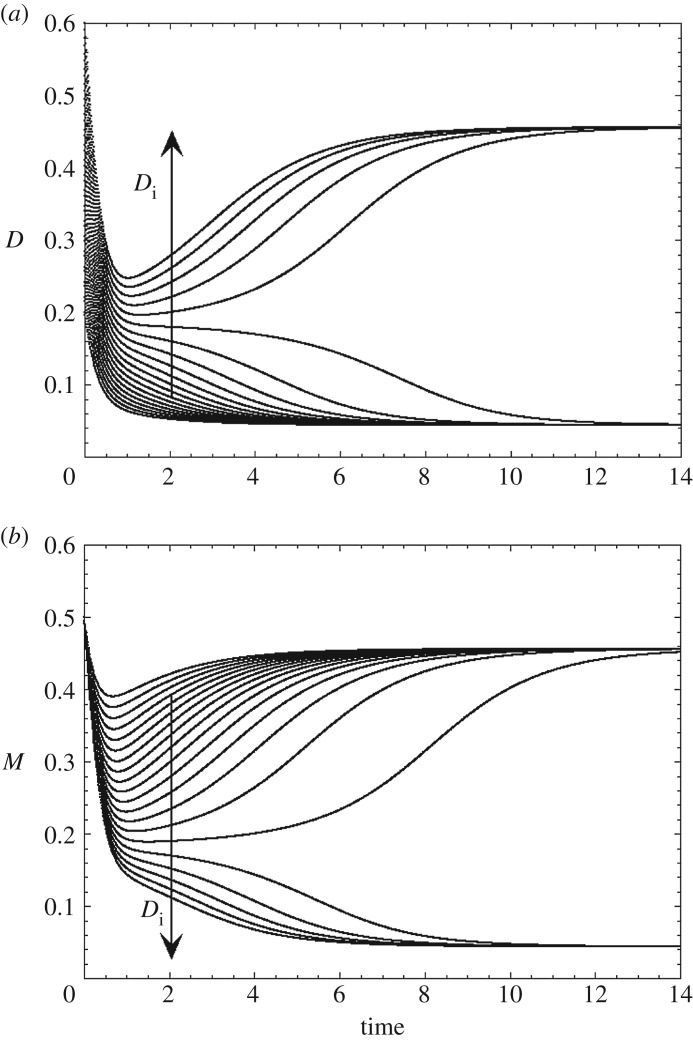
Figure 2.
Transitions between two stable steady states in a model for bipolar disorders [25,26] based on the putative mutual inhibition of two neural circuits promoting depression (D) or mania (M), respectively. The curves show the time evolution of variables D and M for 20 increasing initial values of D, denoted Di. Above a threshold value of Di, D switches abruptly from a low to a high steady state (a), while M concomitantly switches from a high to a low steady state (b).